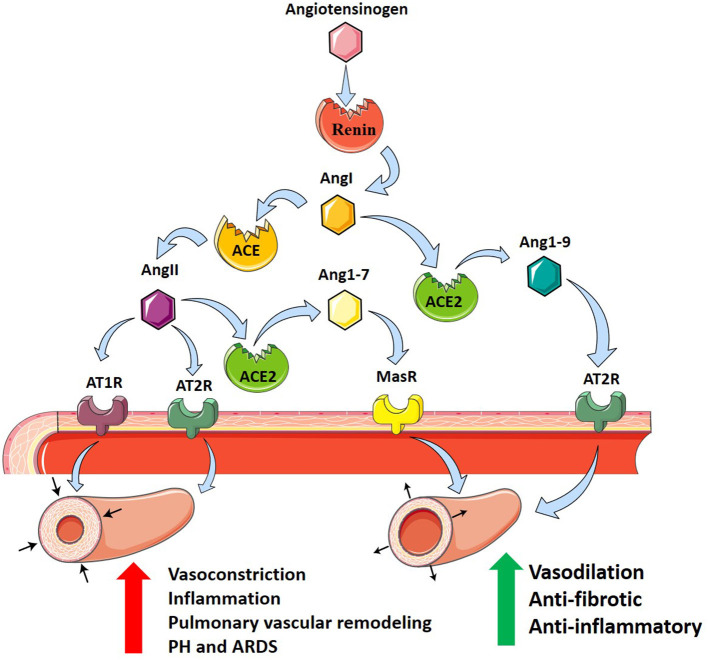
Figure 1.
The renin–angiotensin system and its contribution to PH in ARDS. Angiotensinogen (pink hexagon) is cleaved by renin (red circle) into angiotensin I (AngI, orange hexagon). Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE, orange circle) cleaves AngI producing angiotensin II (AngII, purple hexagon) which binds to angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1R, purple receptor) and angiotensin II receptor type 2 (AT2R, teal receptor), resulting in vasoconstriction, inflammation, and pulmonary vascular remodeling promoting PH in ARDS. Alternatively, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2, green circle) cleaves AngI producing angiotensin1–9 (Ang1–9, blue hexagon) which binds to AT2R, or AngII to produce angiotensin1–7 (Ang1–7, yellow hexagon) which binds to Mas receptor (MasR, yellow receptor). ACE2 counterbalances ACE, protecting against PH in ARDS through anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory actions and vasodilation.