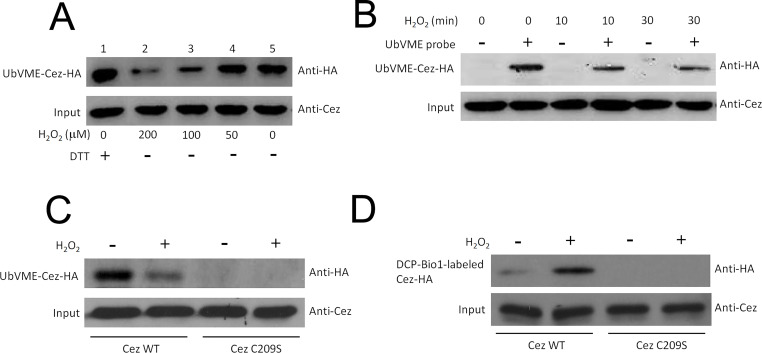
Figure 4.
Oxidation of Cezanne catalytic Cys to the sulfenic acid intermediates. A thiol-reactive probe (HA-UbVME) was used to assess the effects of H2O2 on the catalytic activity of Cezanne. Since this is an irreversible reagent it measures total active site thiol content, not activity. To measure its activity, excess reagent was used and that labeling was measured over the first several percent of the reaction. (A) Cytosolic lysates made from cells expressing Flag-tagged Cezanne were incubated with HA-UbVME probe in the presence of varying concentrations of H2O2. Alternatively, lysates were incubated with probe in the presence of a reducing agent, DTT. Cezanne linked covalently to probe was detected by Western blotting using anti-HA epitope antibodies. Results are representative of two independent experiments. (B, C) HepG2 cells expressing Flag-tagged Cezanne were treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) either in the presence or absence of 100 mM H2O2 or remained untreated as a control. Cytosolic lysates were incubated with HA-UbVME probe or were incubated in the absence of probe as a control. Cezanne linked covalently to probe was detected by Western blotting using anti-HA epitope antibodies. Levels of Cezanne in cytosolic lysates were normalized by Western blot using anti-Cezanne antibodies. (D) Oxidation of Cezanne catalytic Cys to the sulfenic acid intermediate can be captured by DCP-Bio1 probe. HepG2 cells were transfected for 48 h with Cezanne-Flag WT or C209S mutant. Cells were then treated with H2O2 (final concentration 0.3 mM) for 30 min. Extracts were made and divided for two separate reactions: labeling with DCP-Bio1 probe or with the UbVME DUB activity probe. Input represents 30% of extracts used for the DCP-Bio1 reaction.