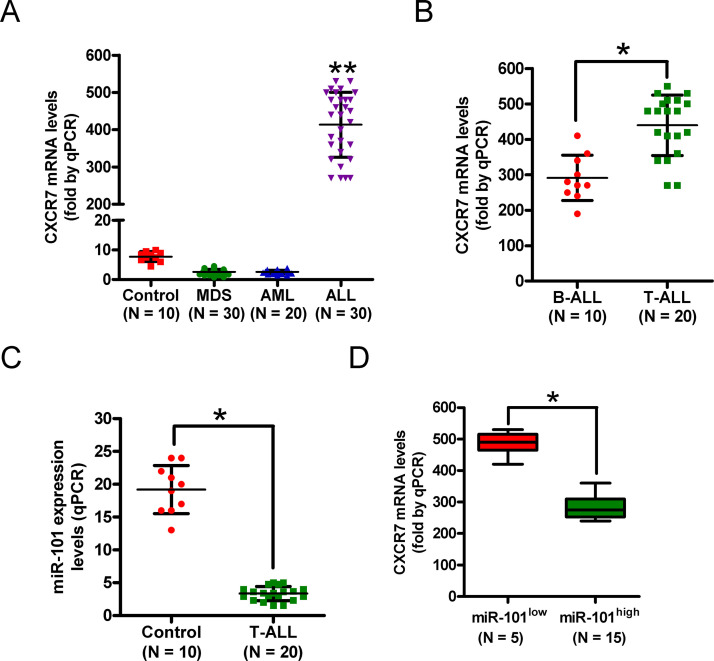
Figure 1.
The levels of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7 (CXCR7) mRNA and microRNA-101 (miR-101) in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) samples. (A) Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analysis of CXCR7 mRNA levels in bone marrow (BM) samples from ALL patients (n = 30) compared with those from healthy donors (control) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS; n = 30) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients (n = 20). (B) mRNA levels of CXCR7 in B-ALL (n = 10) and T-ALL (n = 20) specimens were measured by qPCR assays. GAPDH was used as the endogenous control. (C) qPCR analysis of miR-101 levels in T-ALL samples (n = 20) compared with those from healthy donors (control; n = 10). U6 was used as the internal control. (D) Correlation between CXCR7 level and miR-101 expression in T-ALL specimens. All data are shown as mean ± SD of three separate experiments. *p < 0.05 versus B-ALL group or control group or miR-101low group; **p < 0.01 versus control group or MDS group or AML group.