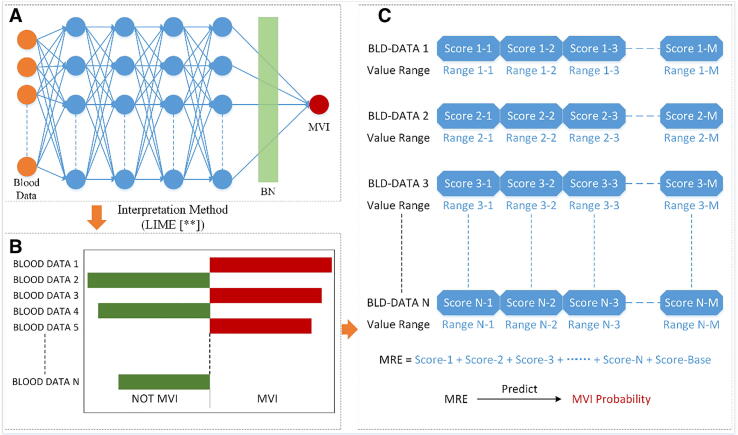
Fig. 1.
The pipeline for the proposed IRP method. (A) Is the fully-connected neural network used for learning the features between the input blood test data and MVI. Each of four blue hidden layers has 32 neurons. Before the last fully-connected layer, batch normalization was applied to accelerate training and avoid overfitting. (B) Shows the result of the explanation of the learner obtained by the interpretation method “LIME”. The length of each column represents the impact of the corresponding variable on MVI (or NOT MVI). (C) Is the scoring model formed from (B). Each variable has an independent score according to its value. The sum of all the scores predicts the risk of MVI. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)