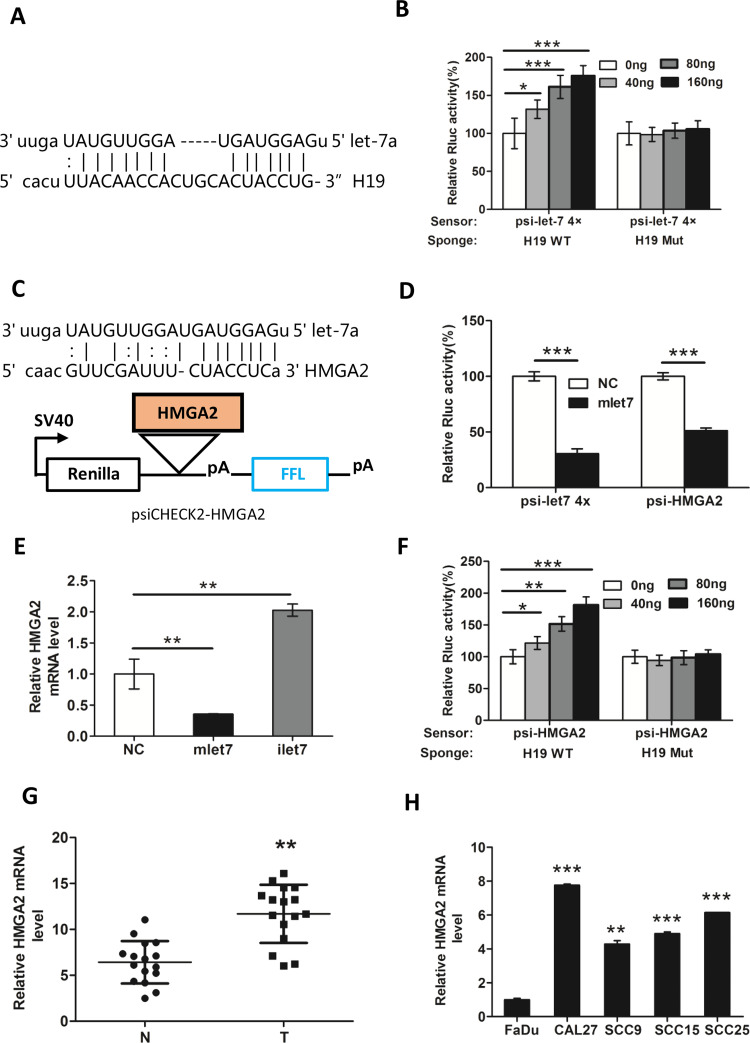
Figure 4.
H19 knockdown decreases the expression of HMGA2 in a let-7-dependent manner. (A) The let-7a binding sites within the full-length transcripts of H19 were validated by the bioinformatics analysis Miranda. (B) let-7 sensor (psiCHECK2-let-7 4×) was transfected into CAL27 cells, together with 0, 20, 40, or 80 ng of sponge plasmid wild type (WT) H19 or mutant (Mut) H19. (C) The diagram represents the psiCHECK2-HMGA2 sensor plasmid. The let-7 binding sites of HMGA2 were inserted to the cloning site. (D) Using psiCHECK2-HMGA2, interaction of HMGA2 and miRNA let-7a was measured by luciferase assay in CAL27. (E) CAL27 cells were transfected with 48 nM control miRNA (NC), let-7 mimic (mlet-7), or let-7 inhibitor (ilet-7). RNAs were extracted 48 h later, and RT-qPCR analysis was performed. (F) let-7 sensor (psiCHECK-HMGA2) was transfected into CAL27 cells, together with 0, 20, 40, or 80 ng of sponge plasmid WT H19 or Mut H19. The expression of HMGA2 in (G) TSCC tissues and (H) cell lines was detected by RT-qPCR. GAPDH was probed as the loading control. Numbers are mean ± SD (n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001).