Fig. 1.
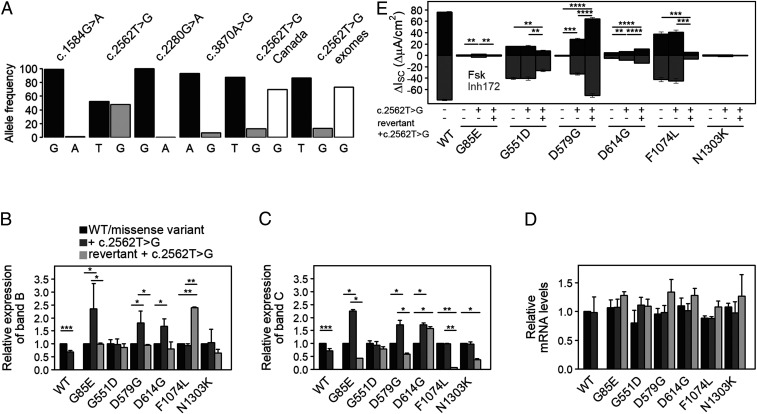
c.2562T > G is a common sSNP in the CFTR gene and augments functional expression of specific disease-causing variants. (A) Allele frequencies of CFTR sSNPs within the general population obtained from the 1000 Genomes Project (24), as well as c.2562T > G (T, black; G, gray) in CF patient cohorts from Canada and the US patients’ exomes (dbGaP, NCBI). Excluding p.delF508, the frequency of the G-allele (white bars) rises. (B and C) Quantification of the expression of CFTR band B (B) and band C (C) from immunoblots (SI Appendix, Fig. S1C) normalized to both NPT (encoded on the same plasmid and used as transfection control) and endogenous ACTB (serving as loading control). Expression levels of each variant with the missense mutation alone were set to 1. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 6 to 9). *P < 0.0046 and **P < 0.00856 (unequal variance t test on log2-transformed data with post hoc Bonferroni’s correction). (D) Steady-state CFTR mRNA levels were measured by qRT-PCR and normalized to the NPT transcript. Values obtained for WT-CFTR were set to 1. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 to 6). (E) Quantification of changes in short-circuit currents (ΔIsc) measured in FRT monolayers transiently transfected with CFTR variants. Transepithelial ion transport was induced with the CFTR agonist forskolin (Fsk), followed by arrest with CFTR inhibitor172 in the presence of a basolateral-to-apical chloride gradient. Revertant refers to a variant with engineered silent codon substitution at the missense codon. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 to 5). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001; Student’s t test.