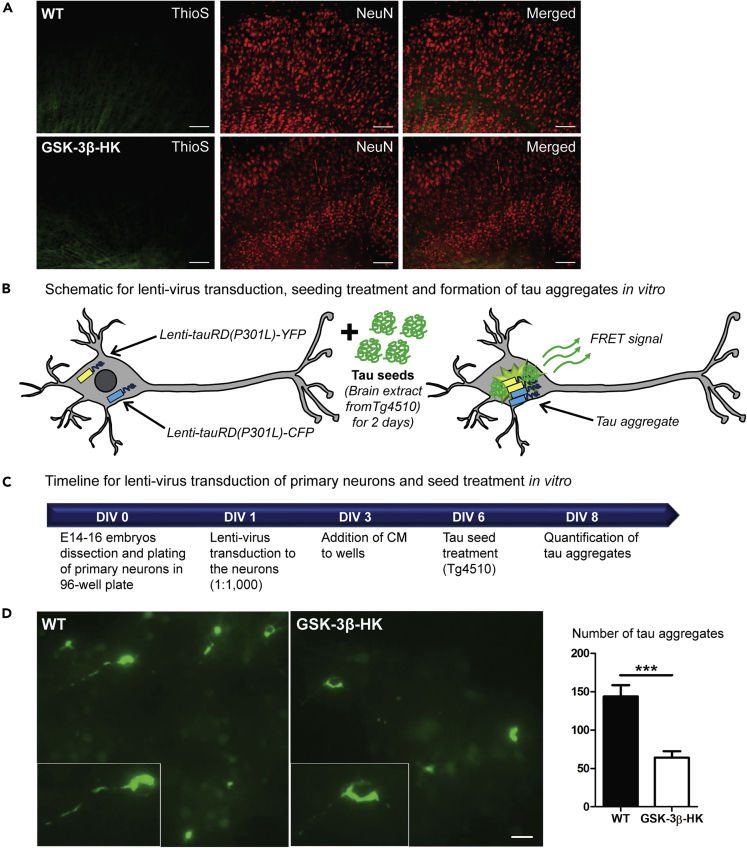
Figure 6.
Reduced levels of GSK-3β decrease tau aggregation in vitro
(A) Representative images of brain sections from WT and GSK-3β-HK mice 6 months after AAV-injection, stained with Thioflavin S (marker of β-sheet-rich amyloid-like aggregated proteins) and immunolabeled for NeuN (neuronal marker). No tau aggregates were observed.
(B) Schematic representation of tau aggregation assay in neurons: primary neurons from WT and GSK-3β-HK embryos were co-transduced with lentiviruses encoding tauRDP301L-CFP and tauRDP301LCFP, and tau aggregation is initiated by subsequent treatment of the neurons with seeding-competent tau in brain extracts from tau transgenic mice (rTg4510). Tau aggregation in the neurons can be detected by fluorescent imaging as FRET signal.
(C) Timeline for tau aggregation assay: primary neurons from WT and GSK-3β-HK embryos are plated in 96-well plate (DIV0) and transduced with lentivirus (lenti-tauRD(P301L)-YFP and -CFP) (DIV1). Transduction is followed with treatment with rTg4510 brain lysate (DIV6) and imaging of FRET-positive tau aggregates (DIV8).
(D) Representative images and quantification of tau aggregates in primary neuronal cultures at DIV8. GSK-3β-HK neurons showed significantly fewer intracellular tau aggregates compared with WT neurons. Inserts show tau aggregates formed intracellularly in WT and HK neurons in culture. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, N = 22 embryos: 10WT, 12HK, 3–5 wells plated neurons per embryo. Two-tailed Student's t test, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Scale bars: 100 μm (A) and 20 μm (D).