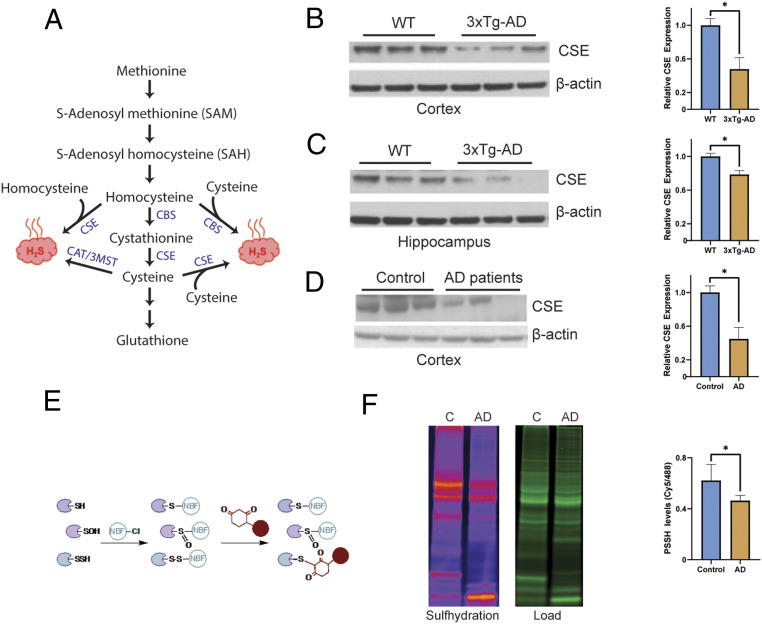
Fig. 1.
Cystathionine γ-lyase expression is decreased in AD. (A) The reverse transsulfuration pathway in mammals. Homocysteine, generated from dietary methionine, is condensed with serine to generate cystathionine by CBS. Cystathionine is acted on by CSE to produce cysteine. Cysteine can either be utilized to synthesize GSH and other sulfur-containing molecules or used as a substrate to generate hydrogen sulfide (H2S). Both homocysteine and cysteine may be utilized to produce H2S. While CSE may generate H2S from either cysteine or homocysteine, CBS produces H2S using a combination of cysteine and homocysteine. The 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase (3MST), in conjunction with cysteine aminotransferase (CAT), a third enzyme, also produces H2S from cysteine. (B) CSE is depleted in the cortex of 24-mo 3xTg-AD mice (n = 3, bars indicate SEM, *P < 0.05). (C) CSE is depleted in the hippocampus of 3xTg-AD mice (n = 3, bars indicate SEM, *P < 0.05). (D) CSE is diminished in the cortex of AD patients (Braak stage 6; n = 3, bars indicate SEM, *P < 0.05). (E) The dimedone switch assay. Proteins were reacted with 4-chloro-7-nitrobenzofurazan (NBF-Cl) to label persulfides, thiols, sulfenic acids, and amino groups. Reaction with amino groups specifically results in a characteristic green fluorescence. Next, the NBF tag is switched by a dimedone-based probe, which emits red fluorescence (the Cy5 tag is shown as a red circle), selectively labeling persulfides. The mixture is then run on sodium dodecyl sulfate gels, and signals are detected by fluorescence scanning. (F) Gel scan showing reduced sulfhydration in postmortem human AD brain samples and quantitation (n = 4, bars indicate SEM, *P < 0.05).