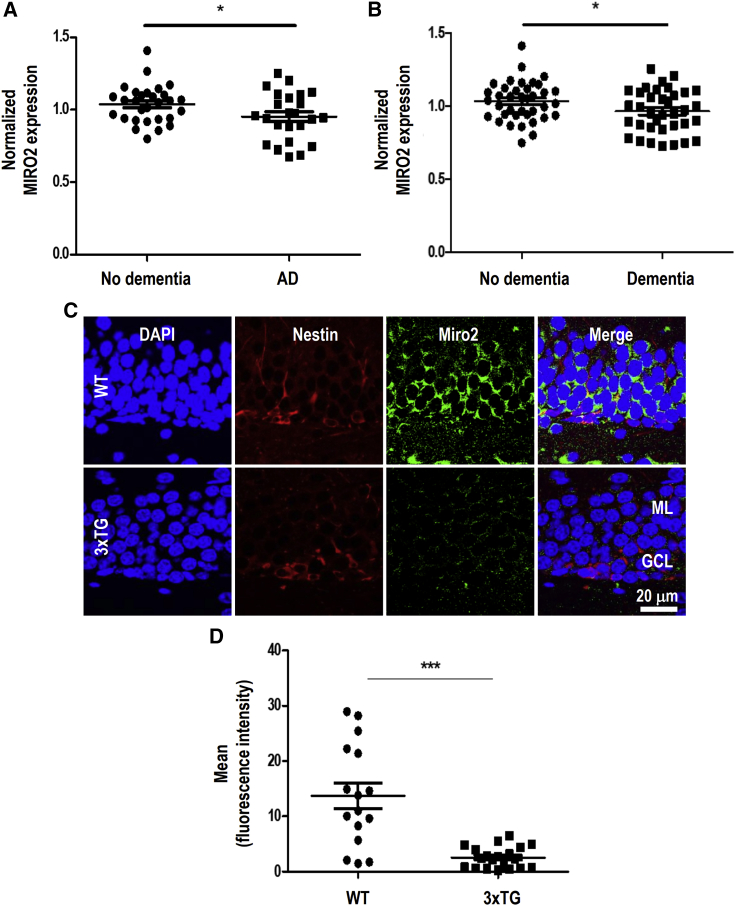
Figure 8.
Expression of miR-351-5p and its target candidate Miro2 in the hippocampus is associated with adult neurogenesis and AD pathophysiology
(A and B) RNA sequencing data from the Allen Brain Institute Aging, Dementia, and Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) study were analyzed for Miro2 expression. The AD group (n = 24) (neuropathological features of AD, including amyloid-β secretion and the presence of amyloid plaques), control group (n = 29), dementia group (n = 36), and non-dementia group (n = 38) were formed. (C and D) To analyze the expression of Miro2 in proliferating cells in the hippocampus of mouse brain, 15-week-old WT and 3xTG AD model mice were examined by immunohistochemistry using anti-Miro2 and anti-Nestin antibody. Images were observed using a confocal microscope, and levels of Miro2 were quantified specifically in Nestin+ cells using ImageJ software. ML, molecular layer; GCL granule cell layer in dentate gyrus. Data in the graphs represent the mean ± SD values (n = 16 cells for WT, 18 cells for 3xTG from three independent experiments). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.