Fig. 2. Hypothesized mechanisms for genome-wide paternal uniparental isodisomy (GWpUPD).
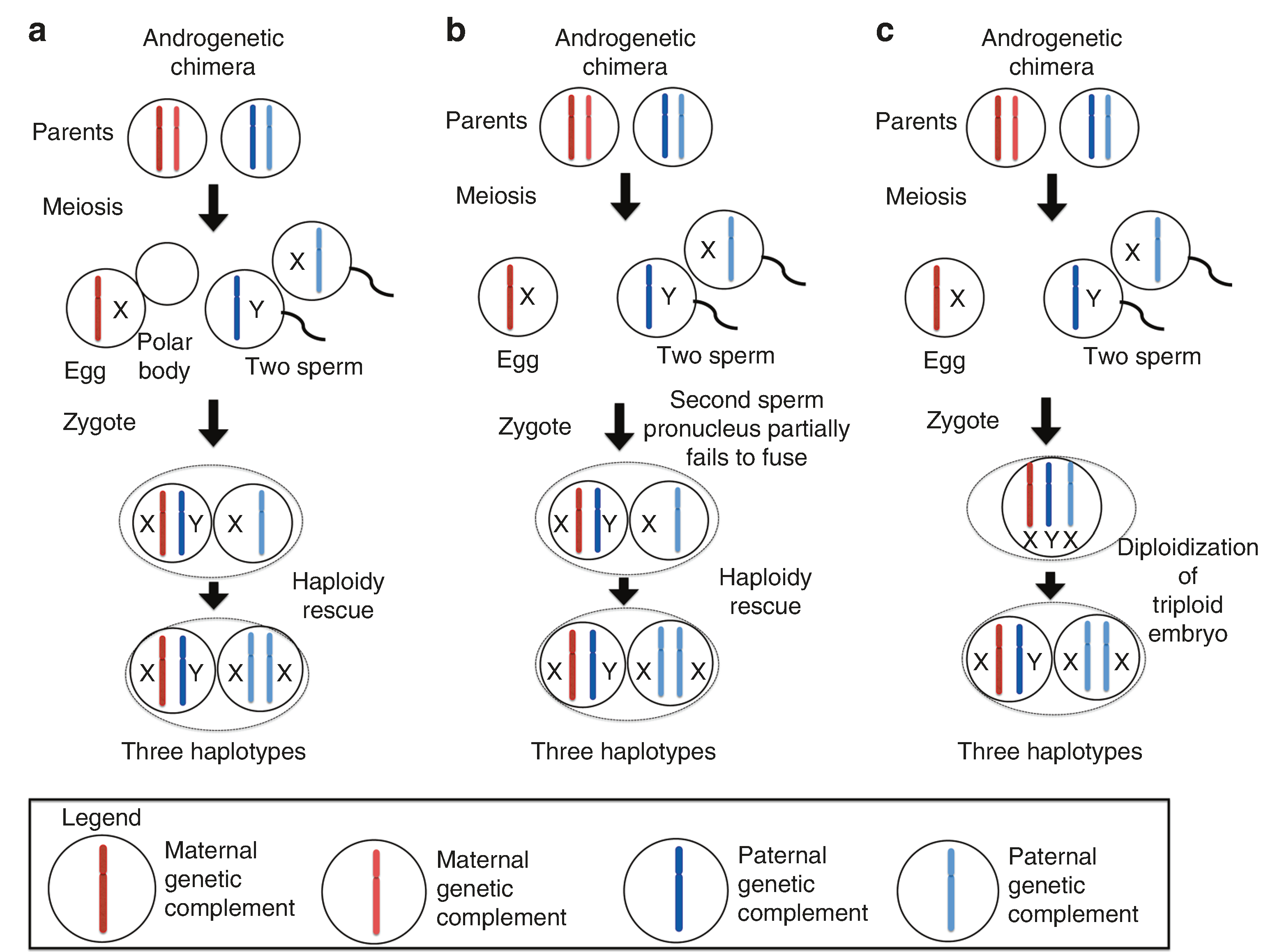
Legend: each bar represents a maternal or paternal haplotype. The X or the Y next to the bar indicates the associated sex chromosome. a Androgenetic chimera. Fertilization occurs between an egg with an anuclear polar body and two sperm. Haploidy rescue occurs leading to two cell line populations with three different haplotypes. b Androgenetic chimera. Fertilization occurs between an egg and two sperm. The second sperm pronucleus partially fails to fuse. Haploidy rescue occurs leading to two cell populations with three different haplotypes. c Androgenetic chimera. Fertilization occurs between an egg and two sperm to create a triploid embryo that undergoes diploidization. This is extremely unlikely as the main mechanism of triploidy is delayed incorporation. The zygote contains three haplotypes.
