FIGURE 2.
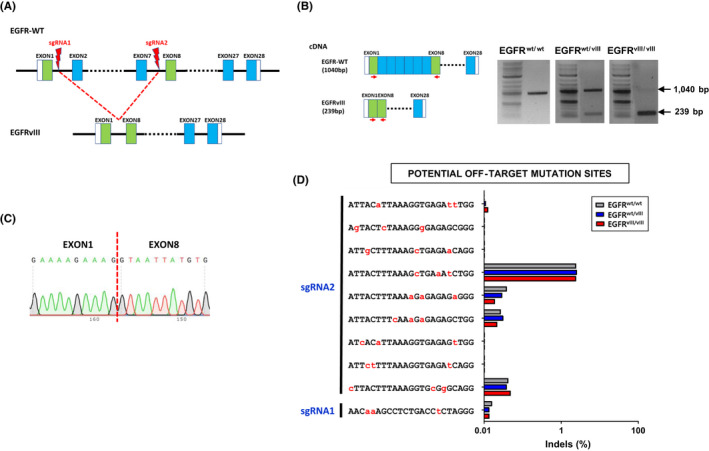
Generation of EGFRvIII‐hESC lines by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. A, Scheme of generation of EGFRvIII mutation by CRISRP/Cas9 system. Two sgRNA binding sites, one in intron 1 and the other in intron 7 of wild type EGFR locus, were indicated. B, Confirmation of monoallelic and biallelic EGFRvIII mutations was confirmed by RT‐PCR using primer pairs recognizing exon1 and exon 8: Primers were indicated as red arrows. Wild type EGFR cDNA produces 1040 bp PCR product, while EGFRvIII cDNA produces 239 bp DNA band. C, Sequencing analysis confirmed the deletion of exon 1 through exon 7 in EGFRvIII mutation. D, Targeted deep‐sequencing analysis revealed undetectable off‐target mutations in both EGFR‐edited clones, EGFRwt/vIII and EGFRvIII/vIII. Prediction of potential off‐target sites with up to three mismatches with the two sgRNA target sequences (sgRNA1‐targeting intron1 and sgRNA2‐targeting intron7 sequences) was performed with CRISPR RGEN Tools website (http://www.rgenome.net/about/): Our EGFR sgRNA target sequences had no potential off‐target sites with one or two mismatches, but had ten potential off‐target sites with three mismatches (one site in intron 1 and 9 sites in intron 7). The mismatched nucleotides were denoted in red and small capital letters in each sequence
