Figure 3.
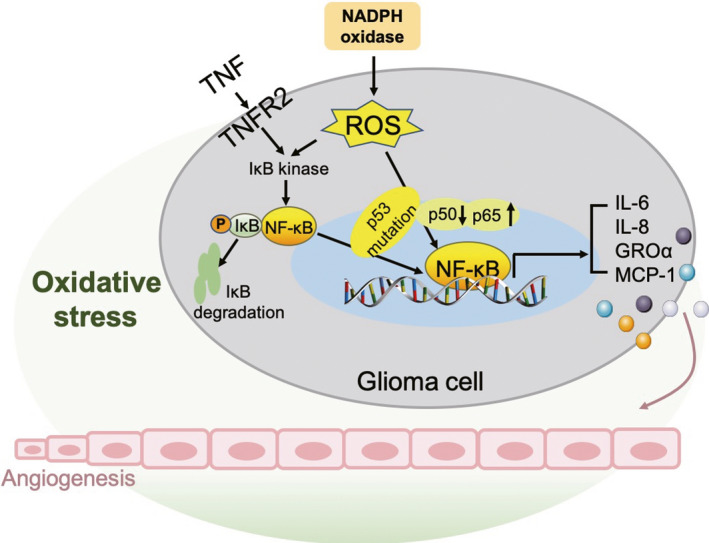
Role of NF‐κB in glioma angiogenesis under a microenvironment of oxidative stress. The ROS produced by NADPH oxidase and TNFR2 mediates the activation of NF‐κB and the main regulatory mechanism of ROS is the phosphorylation and direct oxidation of the NF‐κB subunit (reduce p50 activation and increase p65 activation), and the activation of NF‐κB further depends on the p53 mutation status. The transcriptional activity of NF‐κB for IL‐6, IL‐8, GROα and MCP‐1 promotes glioma angiogenesis. NF‐κB: nuclear factor‐κB; ROS: reactive oxygen species; IL: interleukin; TNFR: tumour necrosis factor receptor; NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; GRO: growth‐regulated oncogene; MCP: monocyte chemotactic protein
