Figure 4.
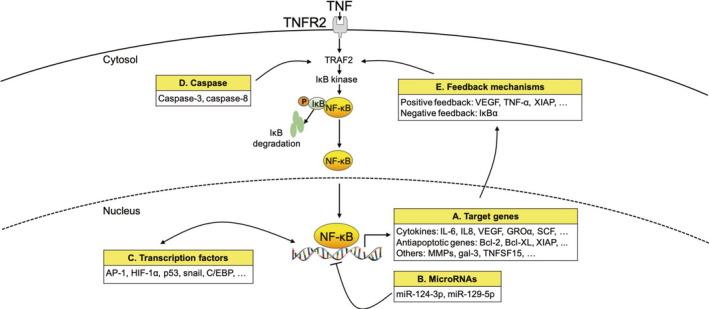
Crosstalk of the NF‐κB pathway involved in glioma angiogenesis with other signalling processes. (A) Target genes of NF‐κB associated with glioma angiogenesis include cytokines such as IL‐6, IL8, VEGF, GROα and SCF; antiapoptotic genes such as Bcl‐2, Bcl‐XL and XIAP; and other genes such as MMP, gal‐3 and TNFSF15. (B) MiR‐124‐3p and miR‐129‐5p block the NF‐κB activation pathways. (C) Numerus transcription factors such as AP‐1, HIF‐1α, p53, snail and C/EBP affect the NF‐κB activation pathways or directly activate the target genes of NF‐κB. (D) Caspase‐3 and caspase‐8 enhance the transcriptional activity of NF‐κB. (E) Positive feedback target genes of NF‐κB such as VEGF, TNF‐α and XIAP further activate the NF‐κB pathway. A significant negative feedback molecule is IκBα. GRO: growth‐regulated oncogene; SCF: stem cell factor; IL: interleukin; TNF: tumour necrosis factor; NF‐κB: nuclear factor‐κB; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; XIAP: X‐chromosome‐linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein; HIF: hypoxia‐inducible factor, MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; TNFSF: tumour necrosis factor super family; Gal‐3: galectin‐3; AP: activator protein; EBP: enhancer‐binding protein
