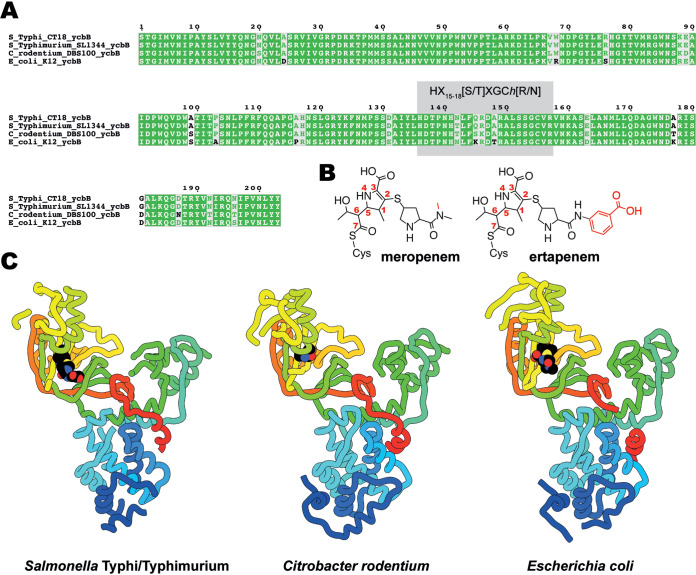
FIG 1.
Multiple-sequence alignment and structures of YcbB. (A) Alignment of amino acid sequences from the catalytic domains of YcbB from Salmonella Typhi CT18, Salmonella Typhimurium SL1344, Citrobacter rodentium DBS100, and Escherichia coli K-12. HX15-18[S/T]XGCh[R/N] (where X represents any residue and h is any hydrophobic residue) is highlighted in gray. (B) Chemical diagrams of meropenem and ertapenem postacylation by YcbB. Differences between meropenem and ertapenem are indicated in red. (C) The structures of S. Typhi/Typhimurium and C. rodentium YcbB are shown in ribbon representation, colored in rainbow from the N terminus (blue) to the C terminus (red), in comparison to the previously solved E. coli YcbB (PDB ID 6NTW [13]) represented in the same scheme. Acylated drugs (ertapenem for S. Typhi/Typhimurium and meropenem for E. coli) are represented by spherical atoms, colored in black and by heteroatom.