FIGURE 1.
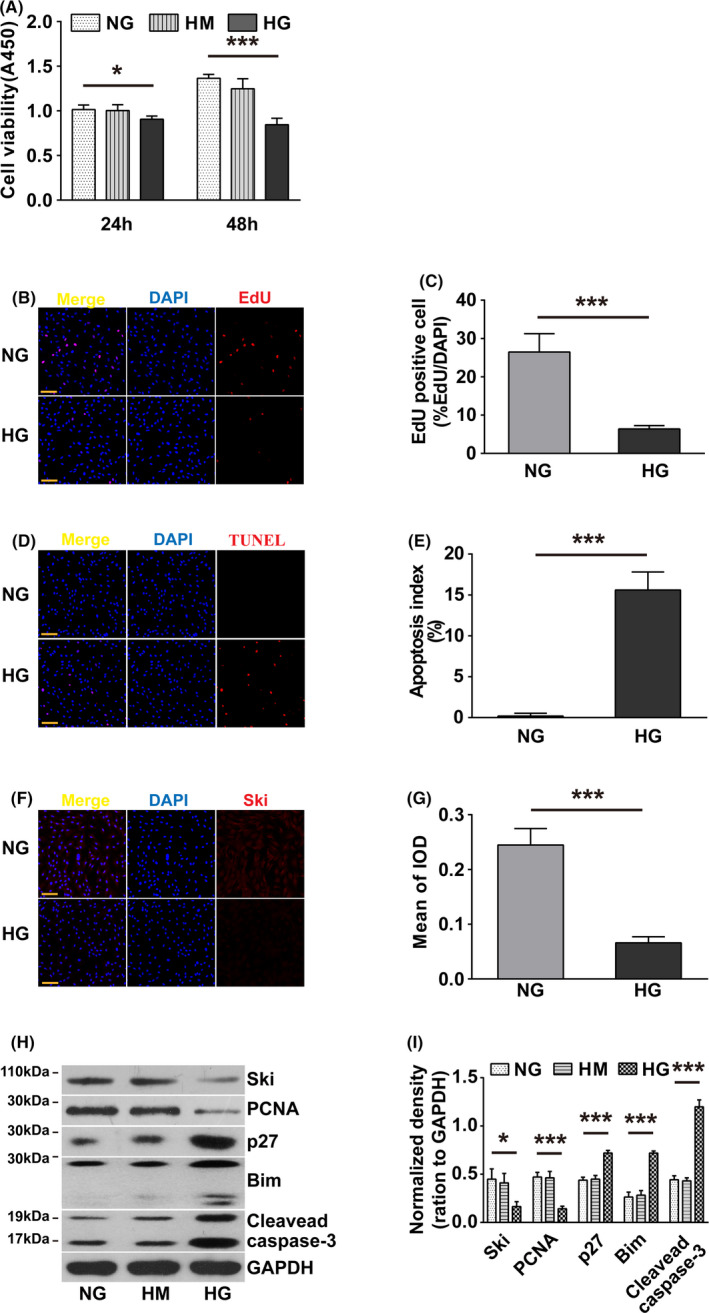
Effect of HG on fibroblast proliferation and apoptosis. Fibroblasts were treated with NG, HG or HM for 24 or 48 hours, respectively. A, A CCK‐8 assay was used to evaluate fibroblast viability. n = 8, The results represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 compared to corresponding NG group, one‐way ANOVA, Dunnett's post hoc tests. Fibroblast proliferation was assessed by an EdU assay (B), and fibroblast apoptosis was tested by a TUNEL assay (D). n = 8, Corresponding quantitative analyses are shown (C) and (E). EdU and TUNEL staining, red; nuclei, blue. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, Student's t test comparing the NG group with the HG group. Scale bars = 100 µm. F, Immunofluorescence staining was conducted to detect Ski expression. Nuclei are indicated with DAPI staining (blue), and Ski expression is indicated by red fluorescence. G, Quantification of immunofluorescence staining; *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, Student's t test comparing the NG group with the HG group. scale bars = 100 µm. H‐I, Western blot analysis of Ski, PCNA, p27, cleaved caspase‐3 and Bim protein expression levels. The results were obtained from three independent experiments. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 compared to corresponding NG group, one‐way ANOVA, Dunnett's post hoc tests
