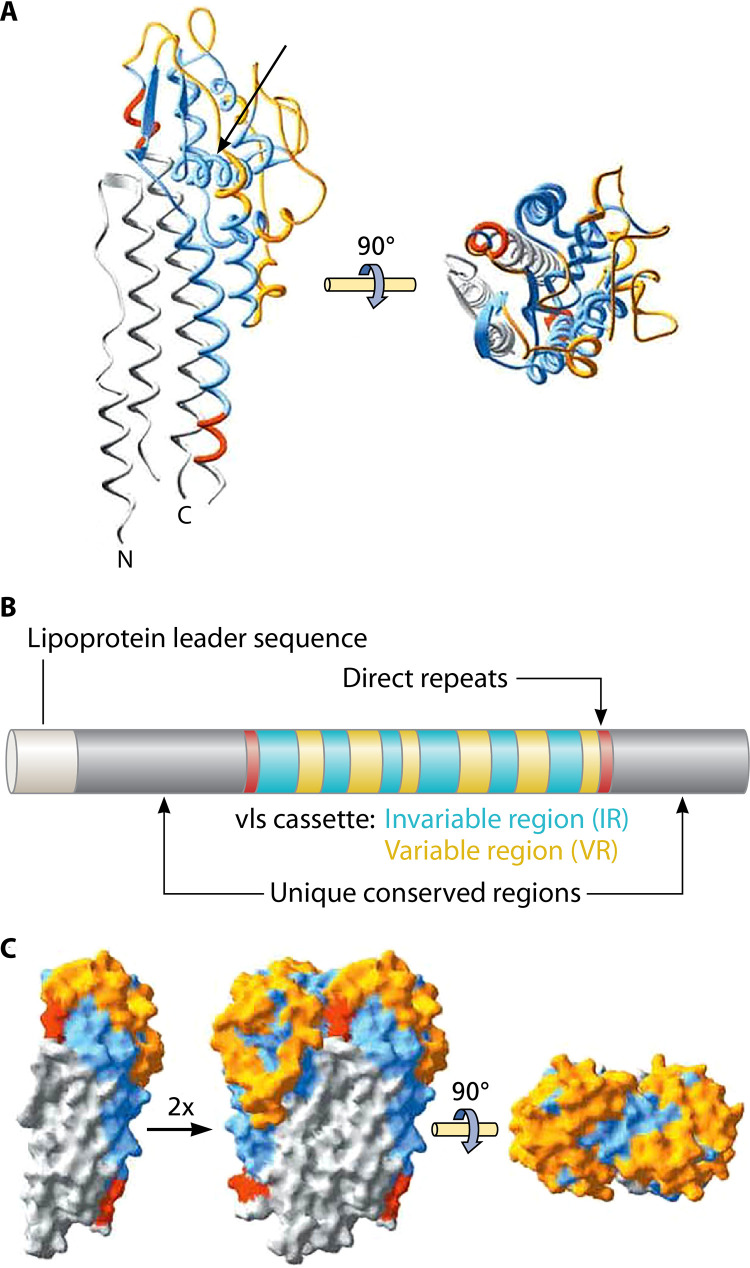
FIG 4.
VlsE primary and tertiary structure. (A) The unique conserved N- and C-terminal regions are colored gray, direct repeats are red, and invariant regions of the cassette are blue, whereas variable cassette regions are orange. IR-VI (arrow) forms an alpha helix buried within the tertiary structure, with little surface exposure. (B) Schematic representation of the primary structure (color code as used in panel A). (C) Dimeric model of VlsE based on the crystal structure, illustrating how the formation of potential dimers could effectively shield invariant regions at the monomer-monomer interface. (Republished from reference 183 with permission of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Note: The figure, as originally published, has been modified here with the addition of an arrow in panel A.)