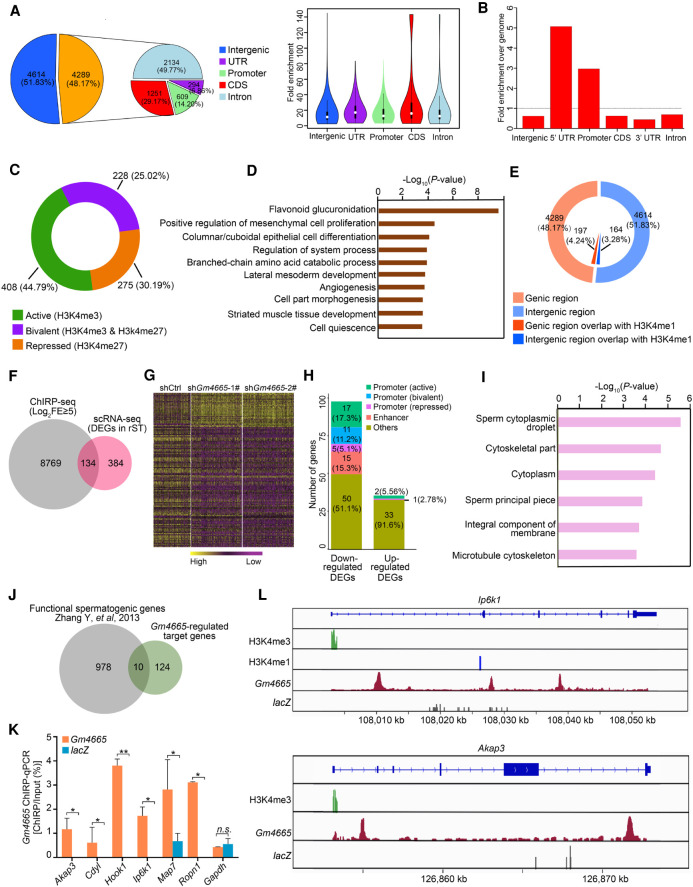
Figure 6.
ChIRP-seq analysis of chromatin interactions between Gm4665 and functional spermatogenic genes. (A) Pie chart showing the distribution of Gm4665-bound peaks in the genome. (B) Intragenic enrichment of ChIRP peaks over the genome. (C) The overlap of Gm4665 ChIRP-seq peaks within promoter regions with the known histone modification markers representative of promoter activities: H3K4me3, correlated with gene activation; H3K27me3, correlated with silencing; coincidence of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3, correlated with “bivalent.” (D) Enriched GO terms for the genes whose promoter was bound by Gm4665 and also marked with the above histone modification markers. (E) The overlap of Gm4665 ChIRP-seq peaks with the known histone modification marker representative of enhancer. (F) Venn diagram showing the number of target genes mediated by Gm4665. (FE) Fold enrichment. (G) Heat map showing 134 Gm4665-regulated target genes in rST populations induced by Gm4665 knockdown. The color key from yellow to purple indicates high to low gene expression levels. (H) The distribution of Gm4665 binding in the regulatory region of these down-regulated and up-regulated genes with Gm4665 knockdown. (I) Enriched GO terms for the 134 Gm4665-regulated target genes. (J) Ten functional spermatogenic genes identified by SpermatogenesisOnline 2.0 database. (K) ChIRP-qPCR validation of chromatin interaction of Gm4665 with six down-regulated functional spermatogenic gene loci. Gapdh gene locus was used as negative control. Data represent the mean ± SEM. (*) P < 0.05, (**) P < 0.01, (n.s.) P > 0.05, Student's t-test. (L) Graphical representation of Gm4665 ChIRP-seq peaks as well as the histone modification ChIP-seq peaks among Ip6k1 and Akap3 gene loci.