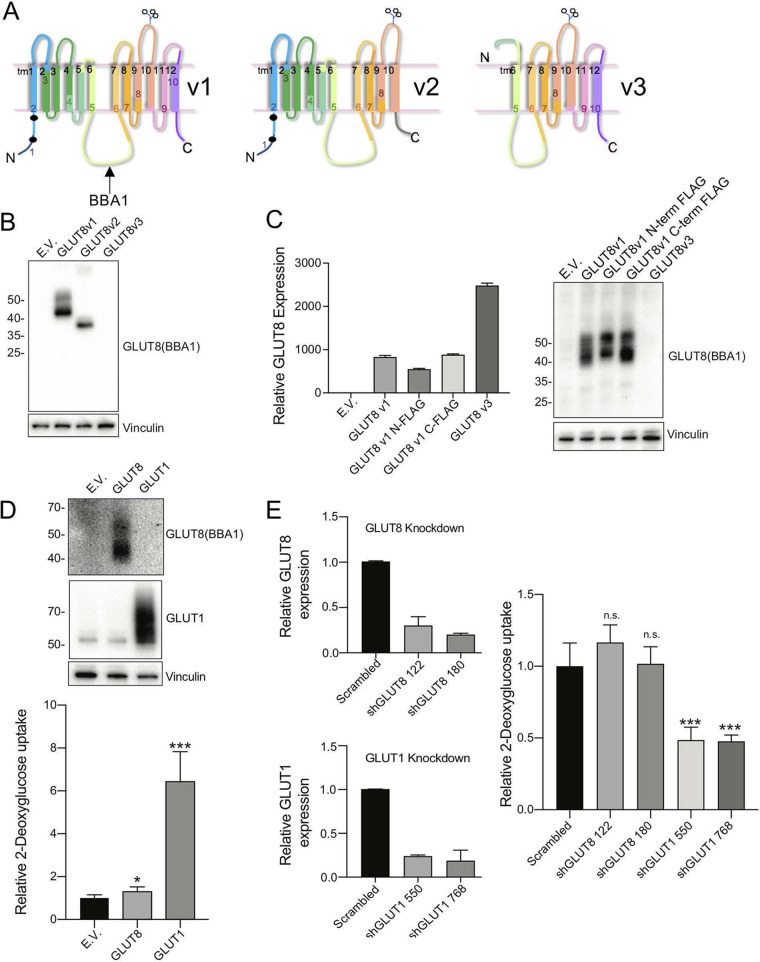
FIG 5.
Assay of properties of variant GLUT8 proteins. (A) Schematic diagram of GLUT8 v1, v2, and v3 putative protein structures, indicating the impact of deletion of exon 9 (v2) and exons 1-4 (v3). (B) Expression of v1, v2, and v3 GLUT8 proteins via Western blotting of lysates from 293T cells transfected with expression constructs. EV, empty vector. (C) Expression of v1, FLAG-tagged v1, and v3, expressed in MB231 cells. RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA from stable GLUT8 overexpressing MB231 cell lines, using a primer set that detects both GLUT8 v1 and v3 isoforms (total GLUT8 assay), for comparison with Western blots of lysates probed with BBA1, an anti-GLUT8 antibody. The protein loading control is vinculin. (D) Assay of glucose transporter activity: gain of function. Western blots (top) of protein lysates from MB231 cells transduced with retroviral GLUT8 or GLUT1 constructs, with the corresponding assay of relative 3H-2DG uptake (bottom). (E) Assay of glucose transporter activity: loss of function. Efficacy of shRNA knockdown of GLUT1 or GLUT8 was assayed (left side) and the impact of knockdown on 3H-2DG uptake assessed (right side). *, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.0001; n.s., not significant. Results are representative of n ≥ 3 assays.