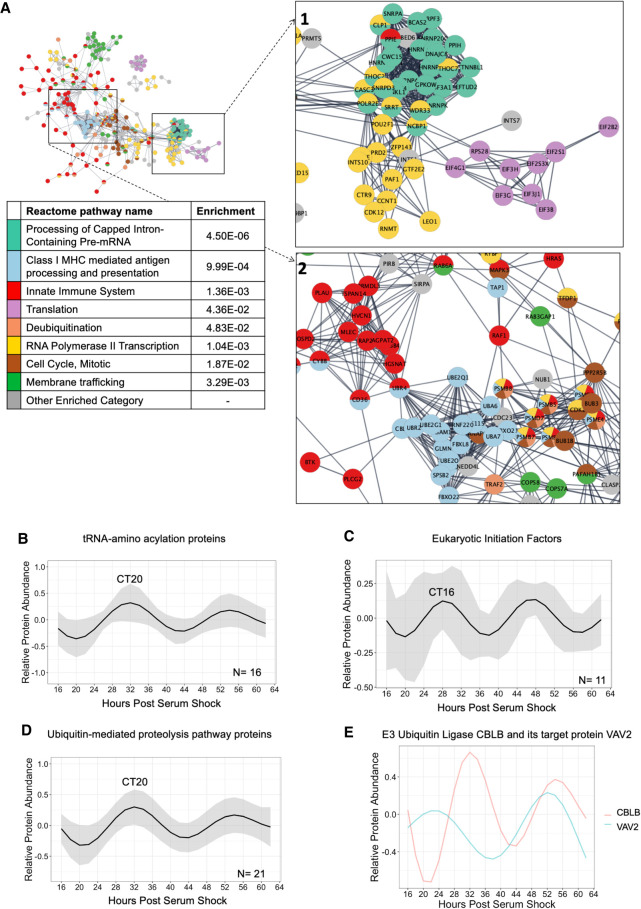
Figure 3.
Functional pathway enrichments indicate late phase post-transcriptional/-translational regulation. (A) A global view of the STRINGdb network of the proteins in enriched Reactome categories that peak in the late wave (CT15–3), with insets focusing on key interactions, including (1) Translation, RNA Polymerase II Transcription, and Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA, and (2) Class I MHC mediated antigen processing and presentation, and Innate Immune System. Interactions shown as strings are filtered to highest confidence interactions (confidence > 0.9). Colors denote independent Reactome categories. Gray coloring represents genes from enriched Reactome categories that did not represent a large proportion of the protein–protein interactome or described redundant categories. (B) An average of the modeled fits of all 16 circadian proteins in the tRNA-amino acelyation reactome category. Shading indicates ±1 standard deviation of models at each time point. The circadian time of the first peak is labeled. (C) An average of the modeled fits of all 11 circadian proteins identified as elogation initiation factors. (D) An average of the modeled fits of all 21 circadian proteins in the ubiquitin-proteasome category, as defined by KEGG. Shading indicates ±1 standard deviation of models at each time point. (E) Modeled fits for the E3 ubiquitin ligase CBLB and a protein it targets for degradation, VAV2.