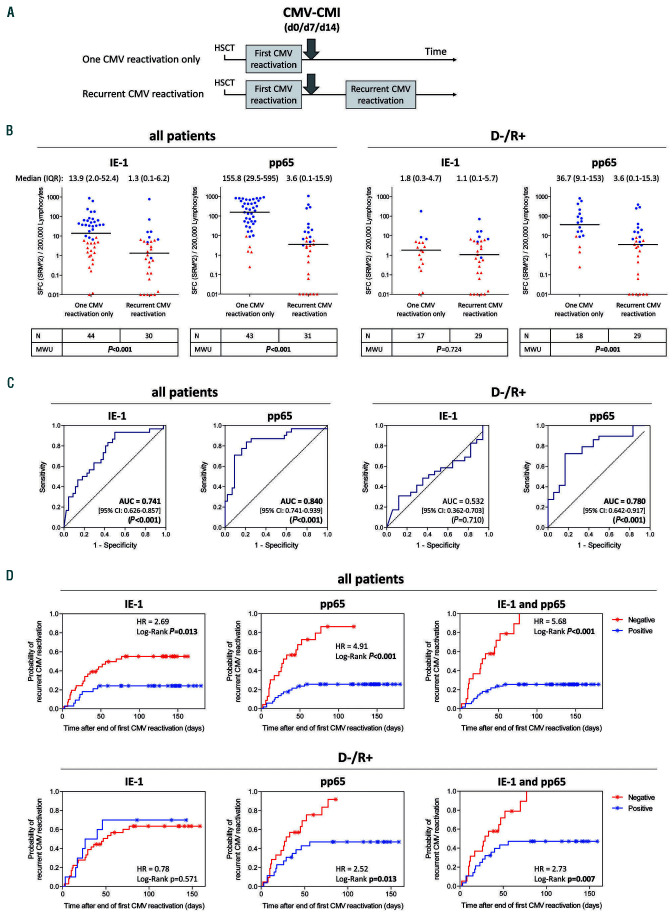
Figure 2.
Legend on following page. Performance of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific cell-mediated immunity measured after the end of a first CMV reactivation to predict freedom from and/or occurrence of recurrent CMV reactivation. (A) Interferon-γ enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISpot) was performed after the end of antiviral therapy for a first CMV reactivation, at up to three time points relative to the end of treatment, namely day 0 (d0), day 7 (d7) and day 14 (d14). The first available measurement was considered for the analysis. (B) Quantitative ELISpot results in response to CMV proteins IE-1 and pp65 were evaluated on the basis of the mean of squareroot- transformed (SRM) spot-forming cells (SFC), as described in the Methods section. Differences in SFC distribution between patients with only one CMV reactivation and those with recurrent CMV reactivation were evaluated using a Mann-Whitney U test. Respective P-values are shown under each graph. For the sake of simplicity, scatter plots are depicted as squared SRM values (SRM^2). The median and interquartile range of the SRM^2 SFC are shown above each graph. Additional information (minimum, maximum, 10th and 90th percentiles) are shown in Online Supplementary Table S3. Due to the log scale representation, values of zero SRM^2 were replaced by 0.01 (y-axis), meaning that baseline values shown at y=0.01 are actually equal to zero. Red triangles and blue dots represent negative and positive tests, respectively, defined according to the rules described in the Methods section. Of note, of the three CMV-negative donor/CMV-positive recipients (D-/R+) with a documented recurrent CMV reactivation and with high pp65-SFC after the first CMV reactivation (251 to 386 SFC/200,000 lymphocytes) one was treated for recurrent CMV although the viral load was below the center-specific threshold (0 or 100 copies/mL) in the 10 days preceding the start of treatment and at all time points thereafter; a second patient had a first treatment initiated for a viral load below the center-specific threshold, after which high pp65-specific SFC dropped dramatically over time before the start of treatment of a CMV reactivation with a viral load above the threshold; the third patient had a lengthy (>3 months) first CMV reactivation with a high sustained viral load (up to 110,000 copies/mL), likely reflecting refractory CMV.55 Importantly, the duration of antiviral therapy for a first CMV reactivation was comparable in patients without and with recurrent reactivation (median [range] duration of 25 [4-94] and 31 [3-77] days, respectively, in all patients [Mann-Whitney U test, P=0.336]; median [range] duration of 31 [4-94] and 34 [7-77] days, respectively, in D-/R+ ptients [Mann-Whitney U test, P=0.677]). (C) Prediction of CMV reactivation recurrence based on IE-1- and pp65-specific SFC counts measured at the end of treatment of a first CMV reactivation was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. Area under the curve estimates, 95% confidence intervals and respective P-values are indicated within each graph. (D) Cumulative probability of CMV reactivation recurrence based on IE-1- and pp65-specific qualitative test results after a first CMV reactivation, evaluated as described in the Methods section. In the case that both IE-1 and pp65 test results are considered (T-TrackR CMV; right panels), a test is positive when at least one IE-1 and/or pp65 test is positive and a test is negative when both IE-1 and pp65 tests are negative. Kaplan-Meier analyses were performed and the respective hazard ratios and P-values are shown within each graph. / indicate censored observations. The median (range) follow-up time after the T-TrackR CMV measurement was 137 (35-180) days in patients with no documented recurrent CMV reactivation (censored). The median (range) time to recurrent CMV reactivation after the T-TrackR CMV measurement was 24 (2-77) days. Moreover, the last recurrent CMV event in the case of a pp65- (and T-TrackR CMV)-positive test result occurred 56 days after the end of antiviral therapy, compared to 77 days in the case of a pp65- and IE-1-negative test result. In (B-D), statistically significant P-values are in bold. CMI: cellmediated immunity; HSCT: hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; IQR: interquartile range; MWU: Mann-Whitney U test; D-/R+: CMV-negative donor/CMV-positive recipient; AUC: area under curve; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio.