Figure 1.
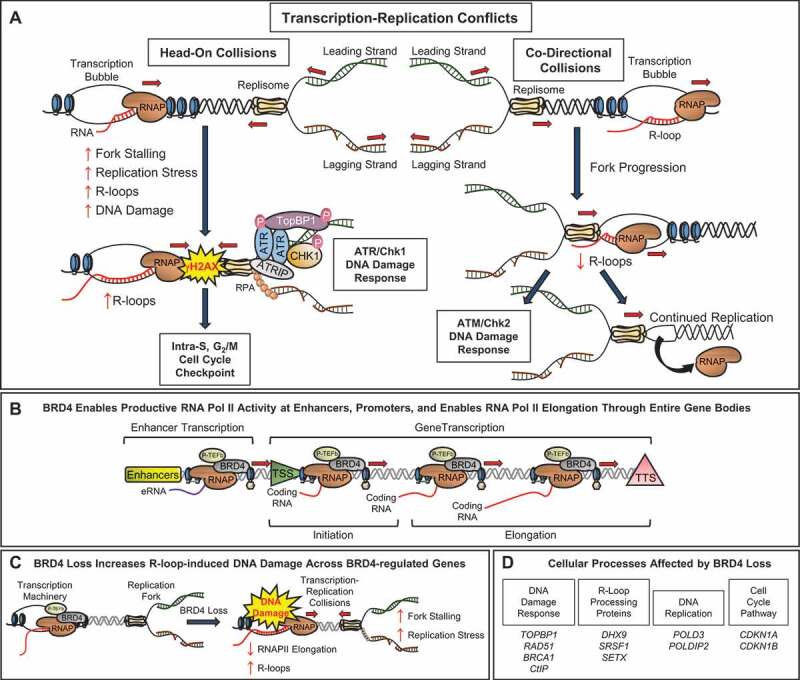
Mechanisms through which BRD4 prevents transcription-replication conflicts in oncogenic cells. (a) DNA damage response signaling pathways associated with head-on vs co-directional transcription-replication collisions. (b) BRD4 facilitates RNA polymerase (RNAP) II activity at upstream enhancer regions, at sites of transcription initiation, and also facilitates productive RNAPII elongation through entire gene bodies. (c) BRD4 loss decreases RNAPII elongation, increases accumulation of R-loops, replication fork stress and stalling, and DNA damage at sites of BRD4-regulated genes. (d) Lists of genes corresponding to cellular processes negatively affected by BRD4 loss
