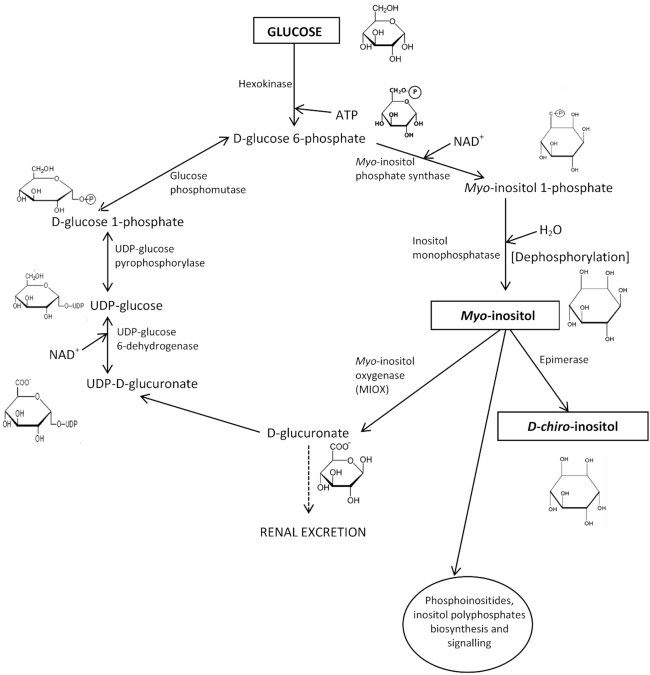
FIGURE 1.
Myo-inositol biosynthesis and catabolism in mammalian tissues. Most tissues can synthesize myo-inositol following phosphorylation of d-glucose to glucose-6-phosphate with subsequent synthesis of myo-inositol-1-phosphate, which, following dephosphorylation, forms free myo-inositol. This can be incorporated into the phosphoinositides cycle, be further catabolized to d-glucuronate for renal excretion or, following a series of enzymatic reactions, be converted back to glucose-6-phosphate. Additionally, myo-inositol can be converted to D-chiro-inositol through the enzymatic action of an epimerase.