Fig. 1.
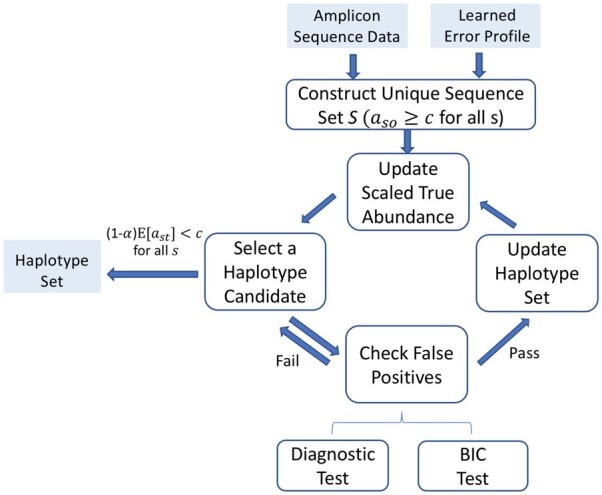
AmpliCI: inferring ASVs from samples. (1) Construct unique sequence set , and put the most abundant unique sequence in haplotype set . (2) Given the current haplotypes , the scaled abundances are estimated for each remaining unique sequence via update function (5), and the haplotype candidate with highest scaled abundance is selected. (3) Verify the approximate BIC improves and the diagnostic probability pmz is small enough, and update . Otherwise, permanently discard candidate and select the next most abundant candidate. (4) Repeat (2)–(3) until the scaled abundance of all remaining unique sequences are below the user-determined abundance threshold c. (5) Output the K haplotypes
