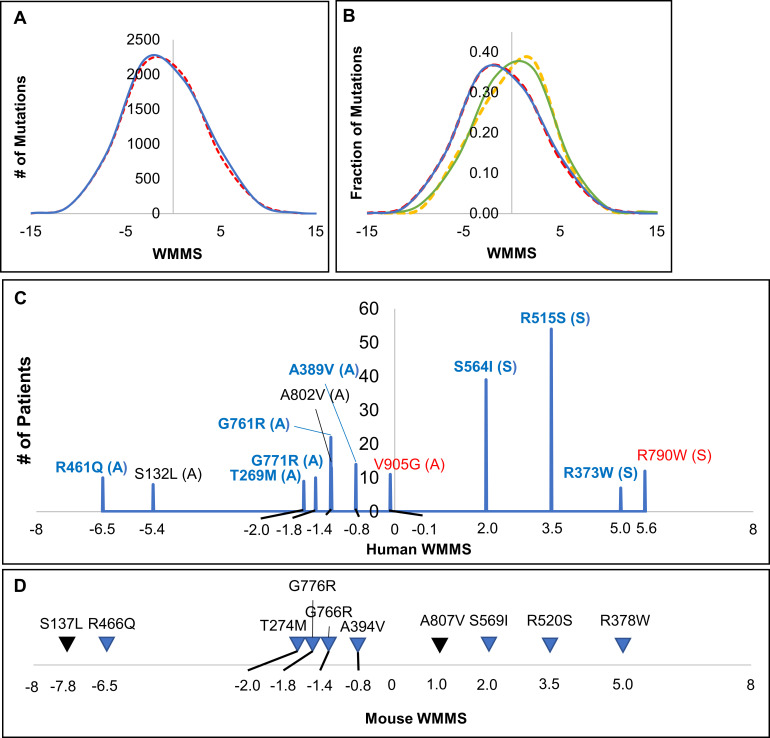
Fig 3. Comparative analyses of Weighted Multiparametric Mutation Scores (WWMS) of Mouse and Human Polymorphisms.
[A] The distribution of all theoretical missense mutations caused by single-nucleotide substitutions in human GLDC cDNA (red dashed line) and mouse Gldc cDNA (blue solid line). [B] WMMS comparison of known pathogenic mutations in human (yellow dashed lines) and their correlates in mouse (green solid line) vs theoretical mutations whose pathogenicity is unknown in both human (red dashed line) and mouse (blue solid line) glycine decarboxylase. [C] The twelve most prevalent human mutations and their hWMMS scores. Attenuated (“A”) or severe (“S”) predictions were assigned based on the mutation’s predicted clinical outcome score (“A” ≤ 5; “S” > 5) based on Farris et al. 2020[16]. Mutations for which the human residue is not conserved in mouse GLDC are shown in red. [D] Mouse counterparts for the most prevalent human mutations and their mWMMS scores. Mutations for which mWMMS is different from hWMMS are shown in black.