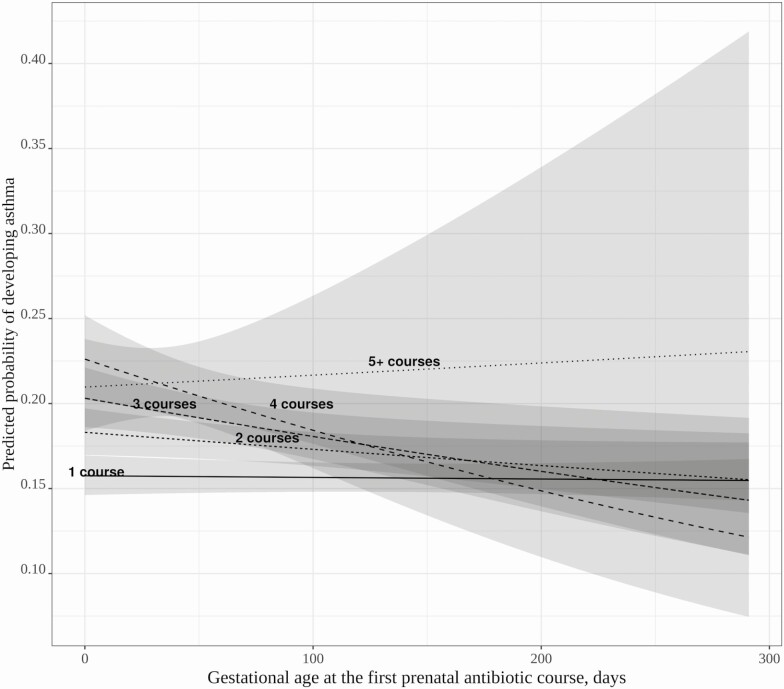
Figure 3.
Effect modification of the timing of the first prenatal antibiotic exposure (gestational age in days) and the cumulative number of prenatal antibiotic courses on risk of childhood asthma. Multivariable logistic regression adjusted for maternal age, asthma, education, smoking, presence of group B Streptococcus infection, delivery method, and infant characteristics including birth hospitalization length of stay, gestational age, birth weight, infant race, sex, and number of living siblings at home. The subjects with ≥ 5 courses of antibiotics have wide confidence bands due to sparse data at later gestational ages. In the group with ≥ 5 courses of prenatal antibiotic exposure, the gestational age of first exposure tended to be earlier with a median of 25 (interquartile range [IQR], 5–51) days, whereas in those with 1–4 courses of antibiotics, median gestational age of first exposure was 95 (IQR, 43–167) days.