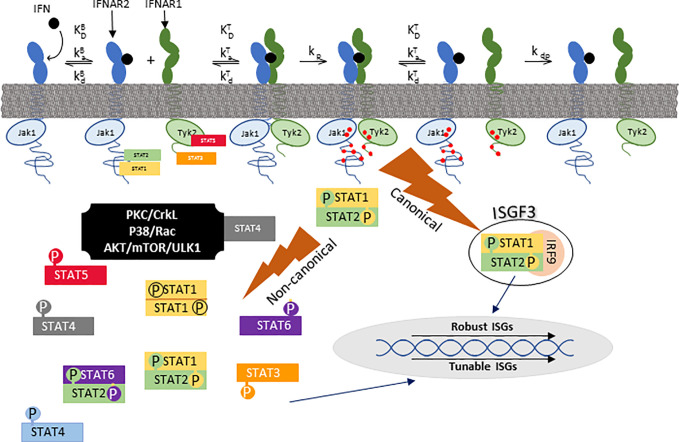
Figure 2.
Canonical and noncanonical IFN signaling. IFN first binds to IFNAR2 after which the IFN/IFNAR2 binary complex recruits IFNAR1 to form a functional ternary signaling complex (IFN/IFNAR1/IFNAR2). Following that, Jak1 and Tyk2 kinases, which are pre-associated with IFNAR2 and IFNAR1 respectively, phosphorylate each other and tyrosine residues on each receptor (red dots) upon which STAT (signal transducers and activators of transcription) family members dock. Canonical signaling consists of a trimer of pSTAT1, pSTAT2, and IRF9 which is referred to as ISGF3 (interferon-stimulated gene factor 3). ISGF3 translocates to the nucleus to bind ISRE (interferon-stimulated response elements) to stimulate transcription of robust ISGs. There are many non-canonical signaling pathways, one of which is formation of phosphorylated STAT1 homodimers that bind to GAS (gamma activation site) promoter elements. ka and kd are association and disassociation rates, respectively. KD is the equilibrium disassociation constant (kd/ka). kp and kdp are rates of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, respectively. KB and KT refer to binary (IFN/IFNAR2) and ternary (IFN/IFNAR2/IFNAR1) complexes, respectively. This figure was adapted from Figure 1 of (24).