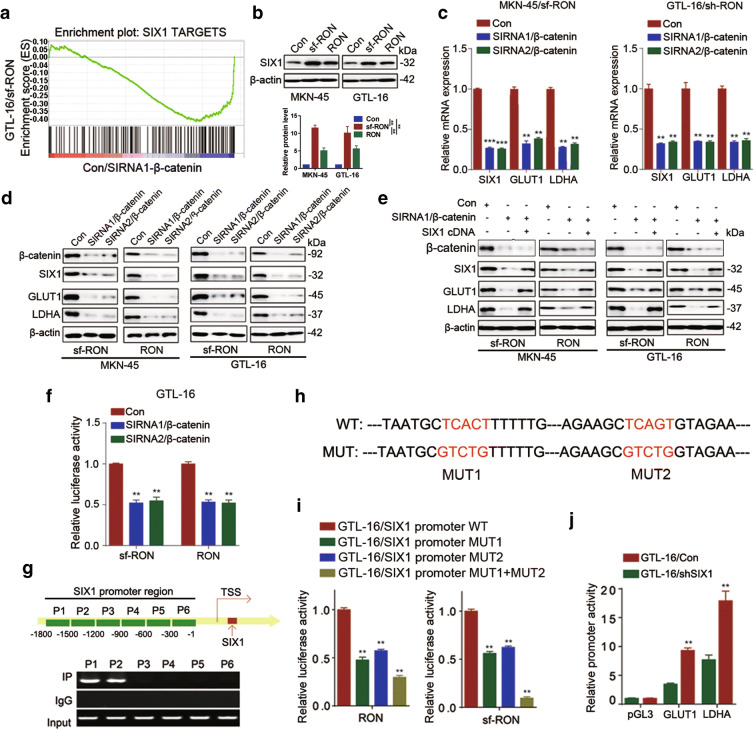
Fig. 4.
SIX1 was a direct target of sf-RON/β-catenin to regulate glycolysis in gastric cancer cells. a GSEA showed high enrichment of the SIX1 pathway from RNA sequencing data. b Western blotting showed that the expression level of SIX1 was enhanced in sf-RON-overexpressing gastric cancer cells, compared with RON-overexpressing and negative control cells. c, d Silencing of β-catenin reduced the expression level of SIX1 in sf-RON-overexpressing and RON-overexpressing gastric cancer cells detected by western blotting and qRT-PCR assay. e SIX1 rescued the silencing of β-catenin on the expression of GLUT1 and LDHA in gastric cells detected by western blotting assay. f Luciferase reporter assay was used to detect the regulation of β-catenin on the promoter activity of SIX1. ** P < 0.01. g, h PCR results of ChIP analysis showed that β-catenin bound to the SIX1 gene promoter region and the map of β-catenin binding sites in the promoter region of SIX1. i Luciferase reporter assay was used for the detection of β-catenin mutant sites in the promoter region of SIX1. ** P < 0.01. j Luciferase reporter assay showed that silencing of SIX reduced the promoter activity of GLUT1 and LDHA. ** P < 0.01