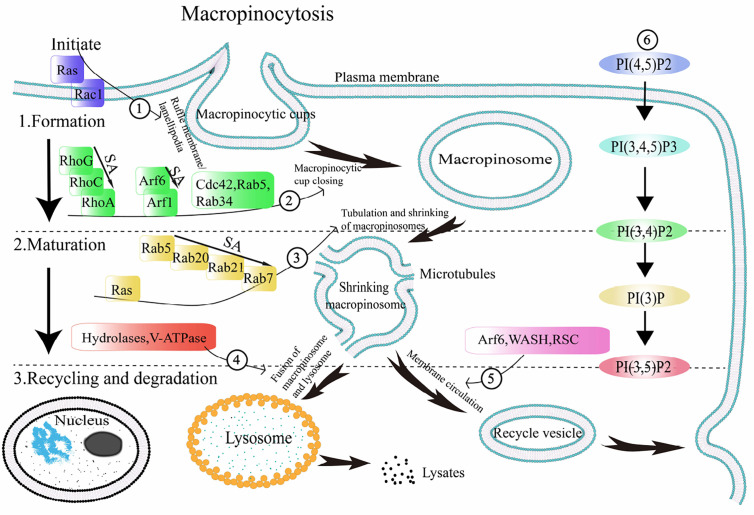
Figure 2.
General process of macropinocytosis. The regulatory factors involved in the process of macropinocytosis are shown in ①-⑥. 1. Macropinosome formation: under the activation of the starting protein Ras, ruffle membrane/lamellipodia is formed, and further developed into macropinocytic cups. Through the sequential activation of a series of related small GTPases and phosphoinositides (PIs), the macropinocytic cups are closed to form macropinosomes. 2. Macropinosome maturation: the sequential activation of a series of related small GTPases and PIs is involved in regulating the occurrence of macropinosome tubulating and shrinking, so that the macropinosome enters a mature state. 3. Degradation and recycle: macropinosomes partially cycle back to the plasma membrane surface and fuse with the membrane, while others fuse with lysosomes and become cleaved. SA: sequential activation. Arf1/6:ADP ribosylation factor-1/6, V-ATPase: vacuolar ATPase, WASH: WASP and SCAR homologues, RSC: retromer sorting complex, PI(4,5)P2: phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, PI(3,4,5)P3: phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate, PI(3,4)P2: phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate, PI(3)P: phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate, PI(3,5)P2: phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate.