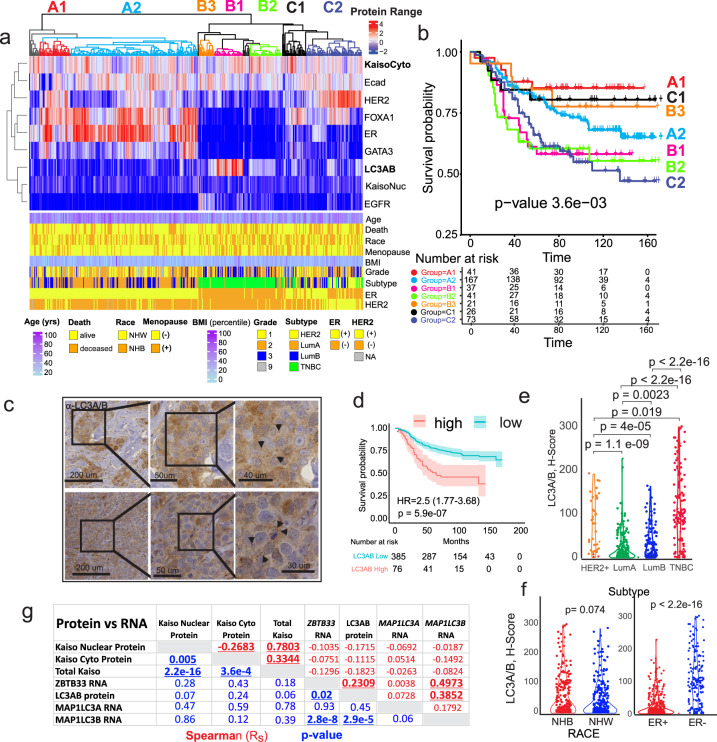
Fig. 3. Quantitative comparison of digitally scored functional and predictive biomarker abundance reveals associations between cytoplasmic Kaiso and the autophagy-related antigen, LC3A/B, that correlate with subtype and survival.
a Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of the nuclear, membrane and cytoplasmic biomarker H-scores for each of (N = 555) patients is shown in correlation with patient clinicopathologic and demographic attributes (below). b Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of specific antigen expression clusters (identified by color code) in a demonstrating associations between cytoplasmic Kaiso, LC3A/B expression, and overall survival in TNBC. c Representative sample of LC3A/B immune-histochemical staining in breast cancer tissues. Arrowhead indicates subcellular puncta noted in the cytoplasm of multiple sections. d Kaplan–Meier survival analysis shows that high LC3A/B cytoplasmic staining is associated with poor overall breast cancer survival. e Like cytoplasmic Kaiso, LC3A/B staining is highly correlated with the more aggressive breast cancer subtypes LumB, HER2, and TNBC with the strongest association with TNBC. f LC3A/B shows a trend of higher expression in NHB versus NHW patients and is significantly more expressed in patients with ER- breast cancer. g Correlation between LC3A/B protein, nuclear Kaiso, cytoplasmic Kaiso, and the RNA levels for LC3A/B, (MAPL1LC3A, MAPL1LC3B), and Kaiso (ZBTB33) showing the strongest correlation between LC3A/B and MAPL1L3B RNA in addition to ZBTB33 RNA and MAPL1LC3B RNA. Spearman correlation is shown in red. p-value for Spearman correlation is shown in blue.