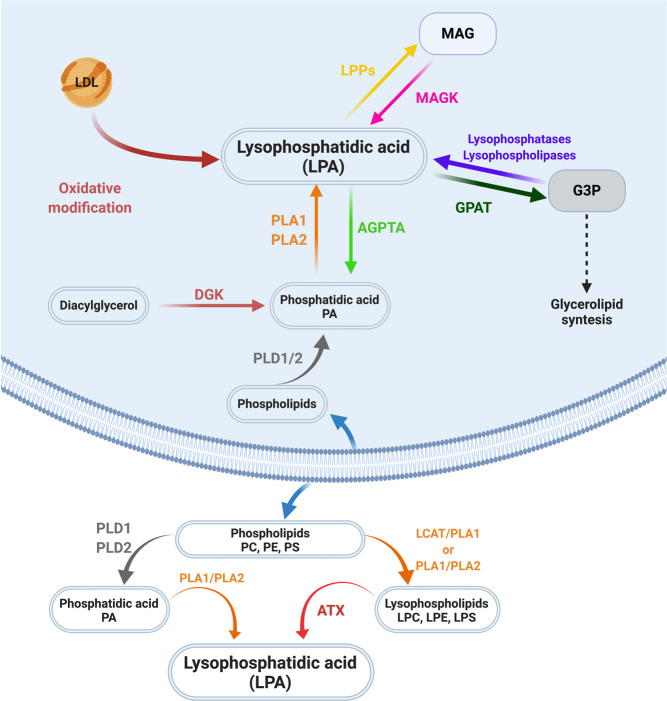
Fig. 1.
LPA intra- and extracellular biosynthesis and degradation. Several mechanisms are implicated in LPA biosynthesis. Several mechanisms are implicated in LPA biosynthesis. Extracellularly, LPA can be produced by two different mechanisms from phospholipids (ATX dependent or independent mechanisms), and signals through six different transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors. Intracellularly, at least four pathways are involved in this process: (1) the monoacyglicerol kinase (MAGK) pathway; (2) the phosphatidic acid-phospholipase A1 (PA-PLA1) or A2 (PA-PLA2); (3) the glycerophosphate acyltransferase (GPAT) synthesis pathway; and (4) the oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) pathway. Finally, these pathways of intracellular LPA synthesis are the same which leads to its degration. Scheme created using Biorender.com