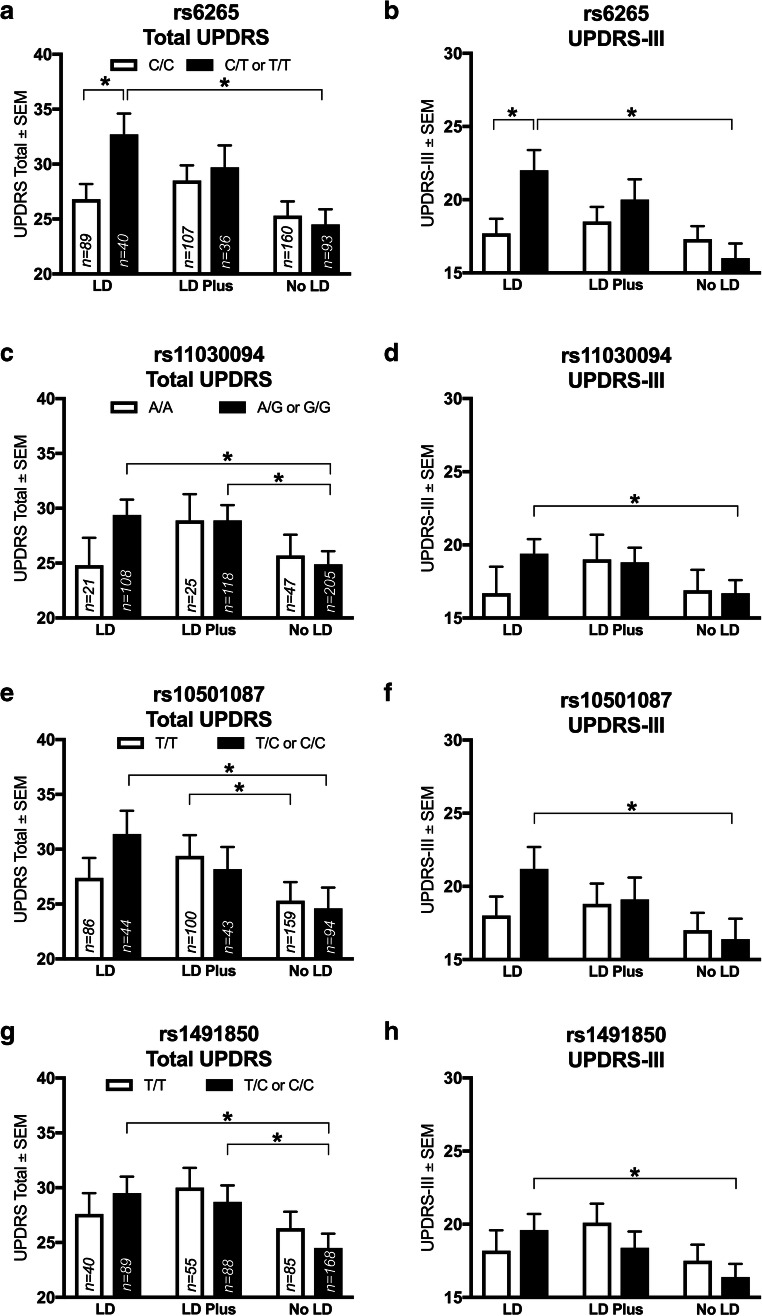
Fig. 2.
BDNF rs6265 SNP and others in the NET-PD LS-1 baseline analysis are associated with differences in outcomes with specific treatment strategies. In subjects on levodopa monotherapy (“LD”), the BDNF rs6265 T allele (C/T or T/T) is associated with worse UPDRS total (a) and part III (b) scores (p = 0.02 and p = 0.03, respectively). Within rs6265 T allele carriers, LD was associated with a worse UPDRS than a no levodopa regimen (“No LD”, A, p = 0.01); similarly, No LD was superior to LD by UPDRS-III in T allele carriers (b, p = 0.01). The rs11030094 G allele also showed a within-genotype difference, where LD is worse than No LD by UPDRS (c, p = 0.002) and UPDRS-III (d, p = 0.01); further, LD plus was worse than No LD by UPDRS (c, p = 0.01). The rs10501087 C/T or C/C subjects show a worse score in association with LD by both UPDRS (e, p = 0.01) and UPDRS-III (F, p = 0.001). In T/T subjects, LD Plus was worse than No LD by UDPRS (e, p = 0.01). For the rs1491850 SNP, LD was worse than No LD within T/C or C/C subjects by UPDRS (g, p = 0.002) and UPDRS-III (h, p = 0.01); further, LD Plus was worse than No LD (g, p = 0.01). Values represent the mean ± SEM. * represents a significant comparison. Darkened bars correspond to “risk” allele carriers; clear bars correspond to no risk allele. Group n values are listed within corresponding bars