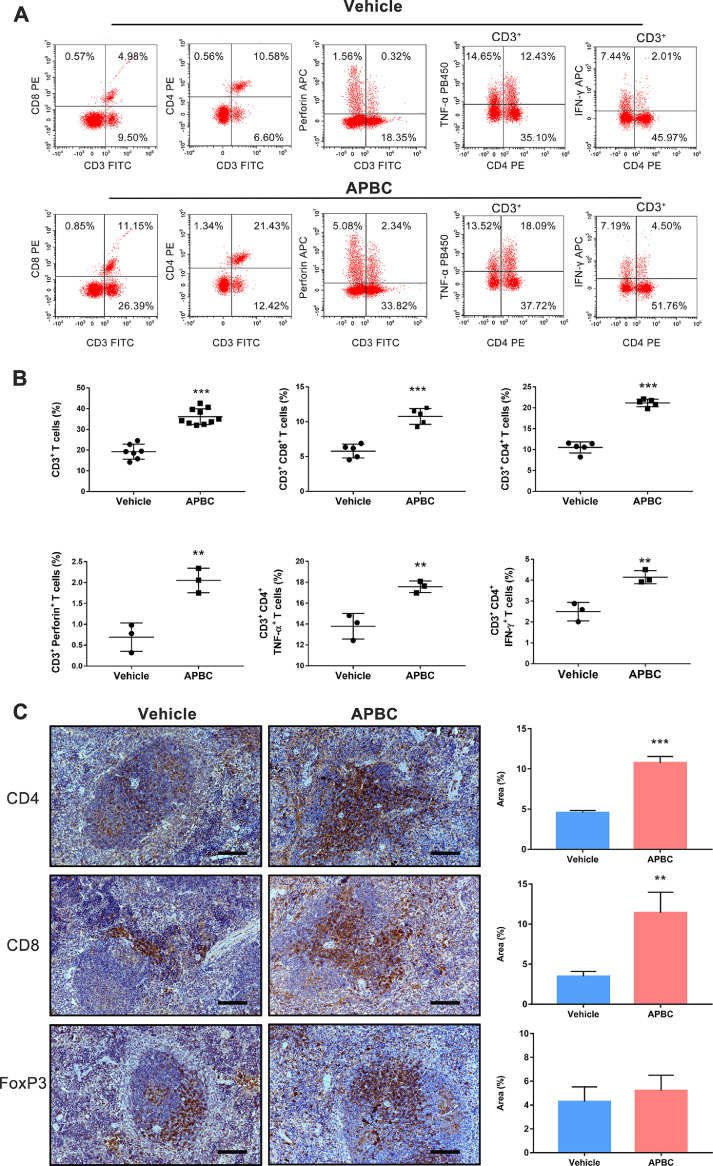
Fig. 7.
Antitumor activity of the APBC is associated with enhanced systemic immunity. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of splenic lymphocytes for T lymphocyte markers and cytokine production. Splenic lymphocytes were purified from APBC (15 mg/kg) and vehicle-treated tumor-bearing mice, and analyzed by flow cytometry for lymphocyte markers CD3, CD4, CD8, intracellular perforin, IFN-γ, TNF-α production. (B) All quantitative data of flow cytometry analysis are represented as means ± SEM, *P< 0.05; **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001, unpaired t test. (C) Immunohistochemical analysis of spleen for T lymphocyte markers after APBC (15 mg/kg)/vehicle therapy. Representative images of specimen stained with anti-CD4, CD8, and FoxP3 antibody. Scale bars = 100 μm, × 200. Immunohistochemical quantification (n = 5) were used Image J. Data were shown as mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P< 0.001 unpaired t test.