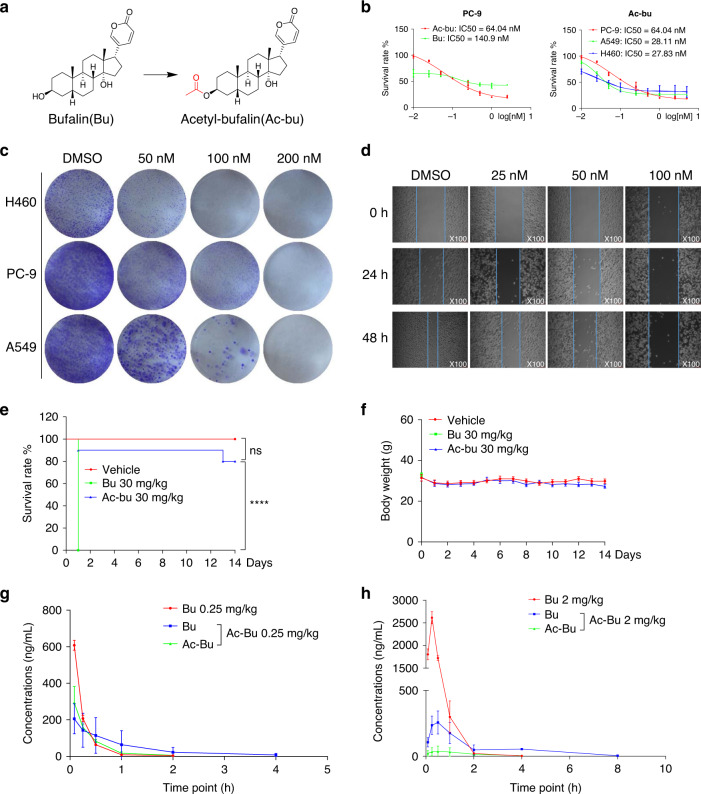
Fig. 1. Acetyl-bufalin changed the pharmacokinetic characteristics of bufalin and enhanced its efficacy.
a Chemical structure of bufalin and acetyl-bufalin. b Human non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells were incubated with increasing doses of bufalin (Bu) and acetyl-bufalin (Ac-bu) for 48 h. Cell viability was determined via MTT assay, and IC50 values were calculated. c Human NSCLC cells were incubated with acetyl-bufalin for 24 h and allowed to form colonies for 1 week. Colonies were then fixed, stained with crystal violet and photographed. d PC-9 cells were plated in six-well plates for 24 h, then scratched and exposed to acetyl-bufalin for 48 h and observed microscopically at ×100 magnification. e The bufalin and acetyl-bufalin groups received an intraperitoneal injection at the dose of 30 mg/kg on the first day, and the mortality and weight of the mice were observed for 14 days. ****P < 0.0001. f Body weight curve of the mice. g Mean concentration-time curves of bufalin and acetyl-bufalin in rat plasma after administration intravenously at a single dose of 0.25 mg/kg (n = 3). h Mean concentration-time curves of bufalin and acetyl-bufalin in rat plasma after administration intraperitoneally at a single dose of 2 mg/kg (n = 3).