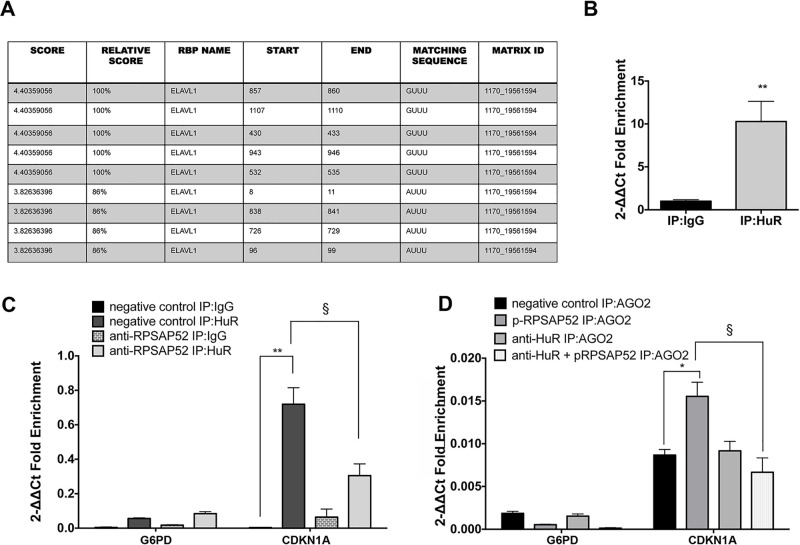
Figure 3.
RPSAP52 promotes the binding of miR-15a, miR-15b, and miR-16 to CDKN1A mRNAs by interacting with HuR RNA binding protein. (A) ELAV1/HuR binding motifs in RPSAP52 sequence by using the “RBPDB binding protein binding motifs database” (rbpdb.ccbr.utoronto.ca). (B) qRT-PCR analysis of RPSAP52 RNA levels in HT-29 cells immunoprecipitated with HuR antibody. IgG was used as a negative control of immunoprecipitation. **p < 0.01compared with IgG:IP samples. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of CDKN1A RNA levels in HCT-116 cells transfected with anti-RPSAP52 oligonucleotide or the relative negative control and immunoprecipitated with HuR antibody. IgG and G6PD enrichment were used as negative controls of immunoprecipitation. **p < 0.01 compared with HCT-116-negative control samples immunoprecipitated with IgG; §p < 0.05 compared with HCT-116 negative control HuR:IP. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of CDKN1A RNA levels in HT-29 cells transfected with scrambled, p-RPSAP52 vector, anti-HuR siRNA, or anti-HuR and p-RPSAP52 vector, and immunoprecipitated with anti-AGO2 antibody. IgG and G6PD enrichment were used as negative controls of immunoprecipitation. *p < 0.05 compared with HT-29 negative control:IP AGO2; §p < 0.05 compared with HT-29 p-RPSAP52:IP AGO2.