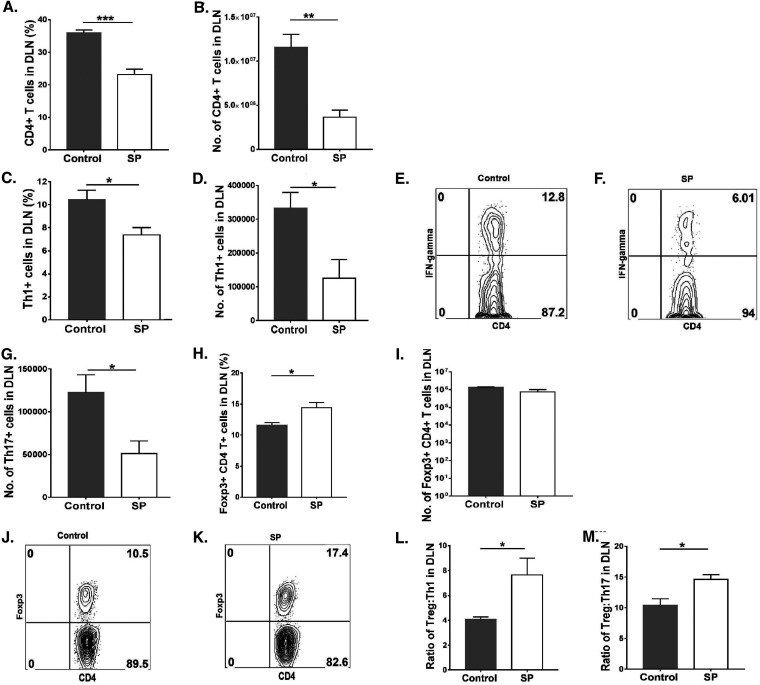
FIG 5.
Feeding SP decreases the level of proinflammatory T cells and enhances the magnitude of anti-inflammatory over proinflammatory cells in the ocular DLN. Orally SP-fed and control C57BL/6 mice were infected with HSV-1, and FACS analysis was performed after 15 days p.i. (A, B) Total CD4+ T cell frequencies (A) and numbers (B) in the DLN. (C, D) Th1 cell frequencies (C) and numbers (D) in the DLN. (E, F) FACS plots representing frequencies of Th1 (CD4+ IFN-γ+) cell infiltration in the DLN. (G) Total numbers of Th17 (CD4+ IL-17A+) cells in the DLN. (H, I) Treg (CD4+ Foxp3+) frequencies (H) and numbers (I) in the DLN. (J, K) FACS plots displaying frequencies of Treg (CD4+ Foxp3+) in the DLN. (L, M) Treg/Th1 cell (L) and Treg/Th17 cell (M) ratios in the DLN. For Th1 and Th17 cell enumeration, stimulation was performed for 4 h with PMA-ionomycin. Data represent mean results ± SEM. All data were analyzed by an unpaired Student t test, and significance levels were determined (*, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001).