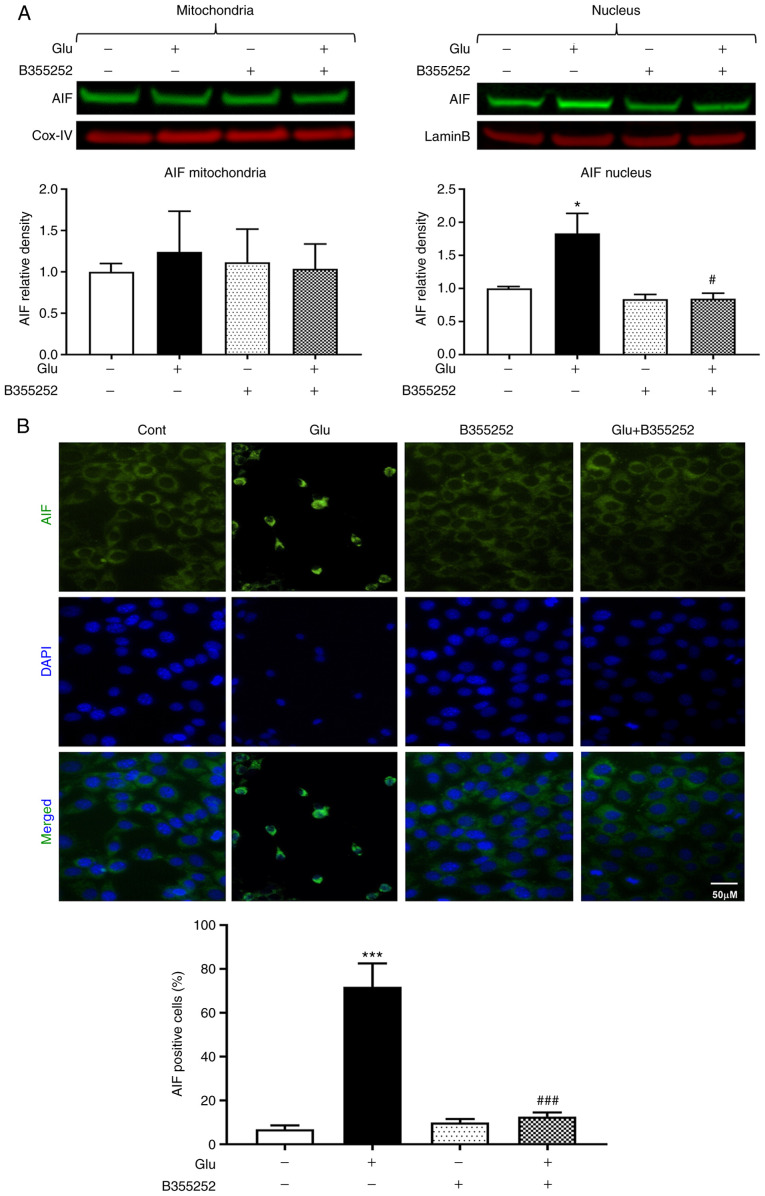
Figure 5.
B355252 prevents glutamate-induced AIF release. (A) Representative western blots and quantitative analysis of the AIF protein bands in the mitochondrial and nuclear fractions of HT22 cells. Mitochondrial AIF levels were similar in the mitochondrial fractions of HT22 cells, regardless of treatment regimen. By contrast, glutamate (2 mM) exposure significantly increased the nuclear translocation of AIF. B355252 (5 µM) pretreatment blocked the nuclear translocation of AIF in cells exposed to glutamate. Values are presented as means ± SD and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison tests. *P<0.05 vs. untreated control; #P<0.05 vs. Glu. (B) Representative immunocytochemical photomicrographs and quantitative analysis of AIF positive cells. Perinuclear staining is observed in the control cells and cells treated with B355252 alone. The translocation of AIF to the nucleus following glutamate exposure is shown by green aggregates in the nuclei, and B355252 blocked the glutamate-induced nuclear localization of AIF. Data is representative of three or more independent experiments conducted in triplicate. Values are presented as means ± SD and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison tests. ***P<0.001 vs. untreated control; ###P<0.001 vs. Glu. Glu, glutamate; AIF, apoptosis-inducing factor; Cox-IV, mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV.