Figure 2. Literature-Derived Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Network.
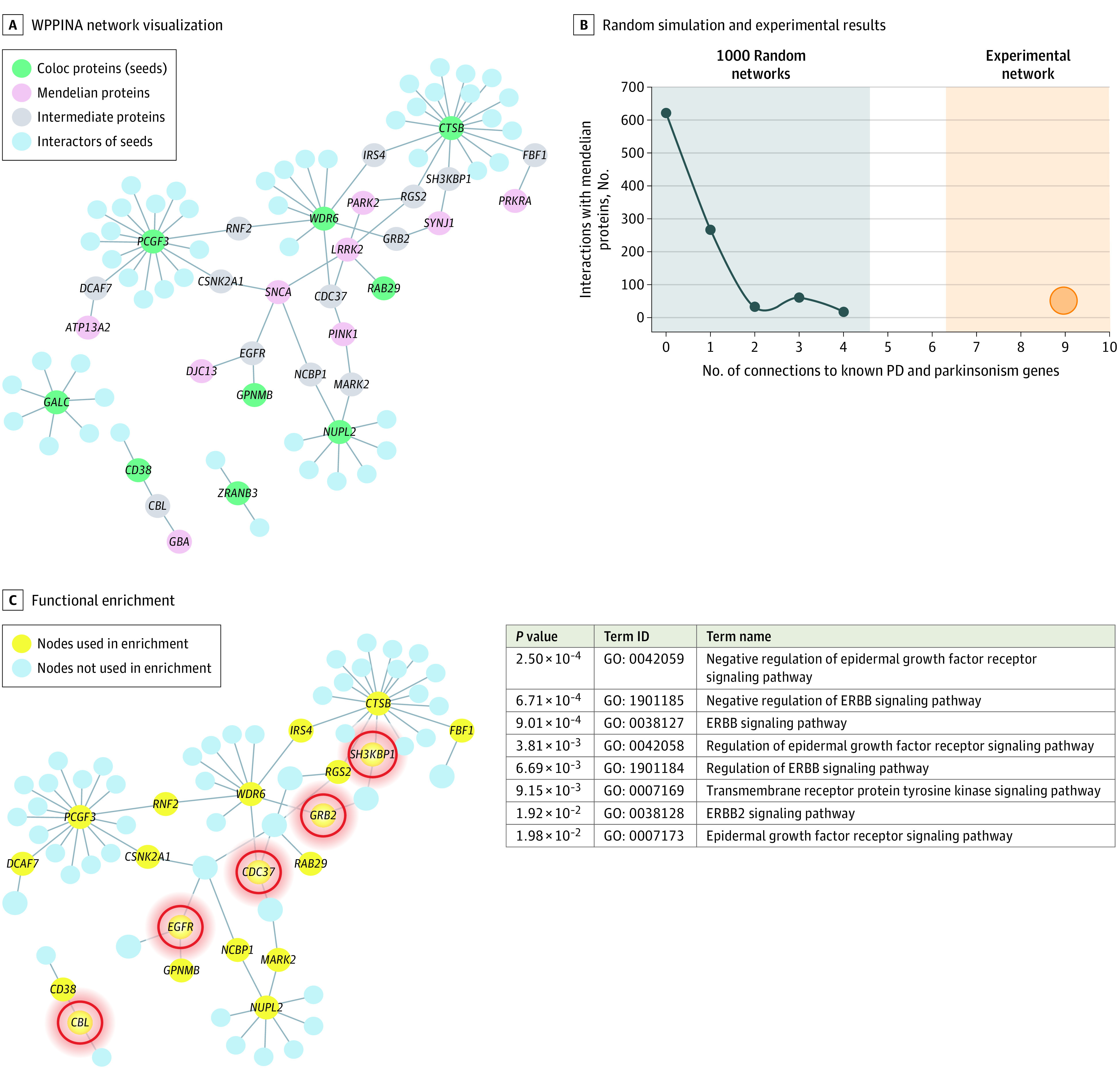
A, Weighted protein-protein interaction network analysis (WPPINA) network visualization of the PPIs specific for the proteins (seeds) coded by the Coloc genes (green nodes). Minor protein interaction partners are shown in blue, while mendelian Parkinson and parkinsonism proteins interacting with parts of the seeds’ interactome are reported in pink. Major interaction partners (ie, they bridge interaction between at least a Coloc protein and a mendelian protein) are labeled in gray. B, The negative control protein network has been randomly sampled to generate 1000 random networks with similar features to the actual Coloc network. These therefore included same or similar number of seeds (9 seeds) to the Coloc protein network and were matched to the mendelian protein network to quantify the number of mendelian proteins able to interact with the random seeds’ interactome. C, Nodes highlighted in yellow (Coloc proteins connected to mendelian Parkinson disease (PD) proteins and internodes) were used to run functional enrichment. The most specific terms of enrichment are reported in the table with their adjusted P value, gene ontology (GO) term identifier, and name. The proteins associated with the enrichment of the terms reported in tables are circled in red.
