Figure 2.
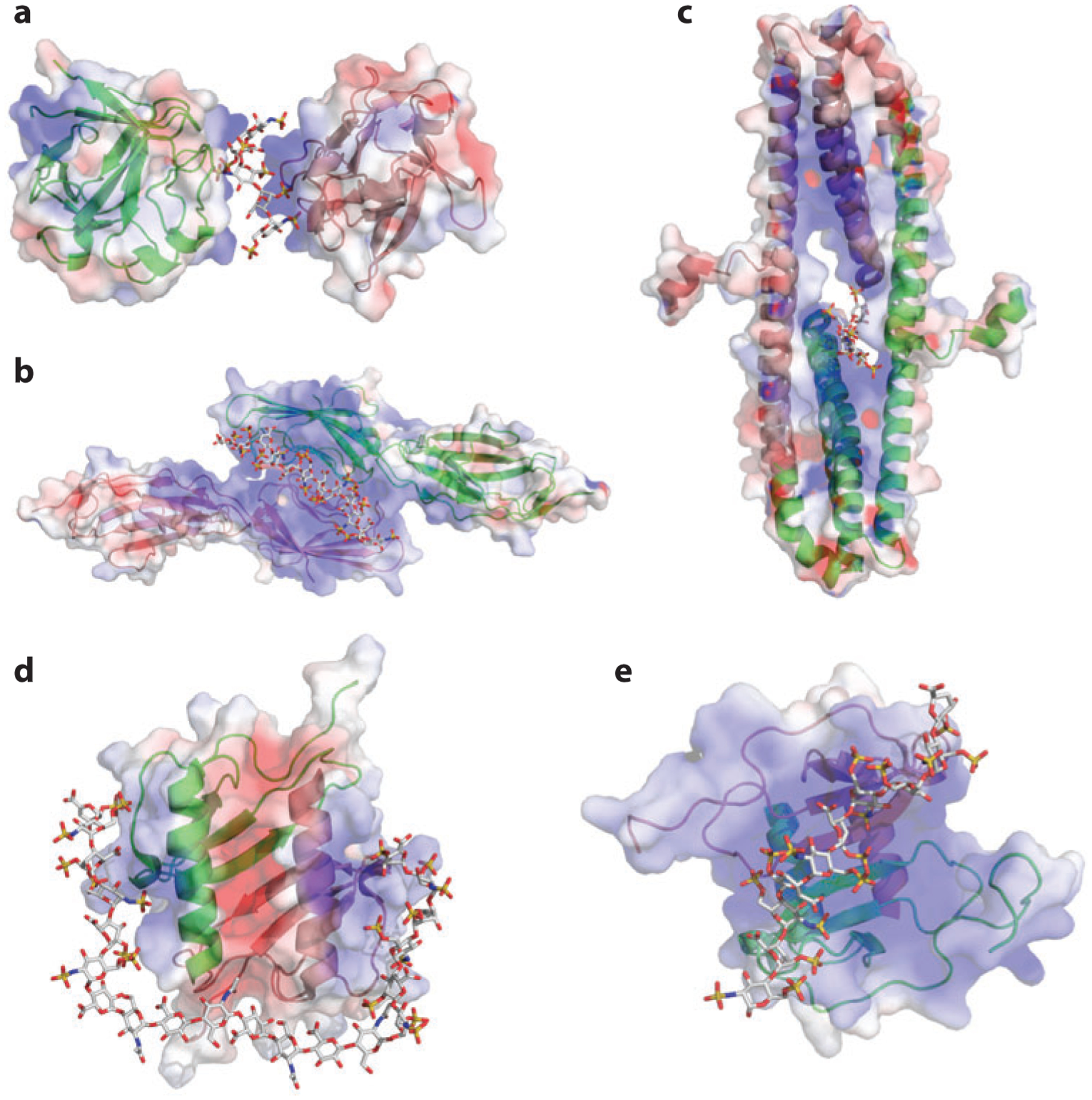
Heparan sulfate (HS)–induced HS-binding protein oligomerization. In the three-dimensional drawings, one monomer is in green and one in pink; in the surface representations, positive electrostatic potential is in blue and negative electrostatic potential is in red. For the oligosaccharide, carbon is gray, oxygen red, nitrogen blue, and sulfate yellow. (a) Structure of FGF1 (fibroblast growth factor 1) dimer and bound oligosaccharide [Protein Data Bank (PDB) identifier 1AXM]. (b) Structure of the dimeric V-C1 domains of RAGE (receptor for advanced glycation end products) (PDB 4IM8). The dodecasaccharide is manually modeled into the structure on the basis of the observed partial electron density. (c) Structure of the dimeric E2 domain of amyloid precursor–like protein 1 (APLP-1) and bound oligosaccharide (PDB 3QMK). (d) Structure of dimeric interleukin-8 (PDB 2IL8) and a modeled oligosaccharide (degree of polymerization: 20). (e) Structure of dimeric CXCL12 (PDB 2NWG) and a modeled decasaccharide.
