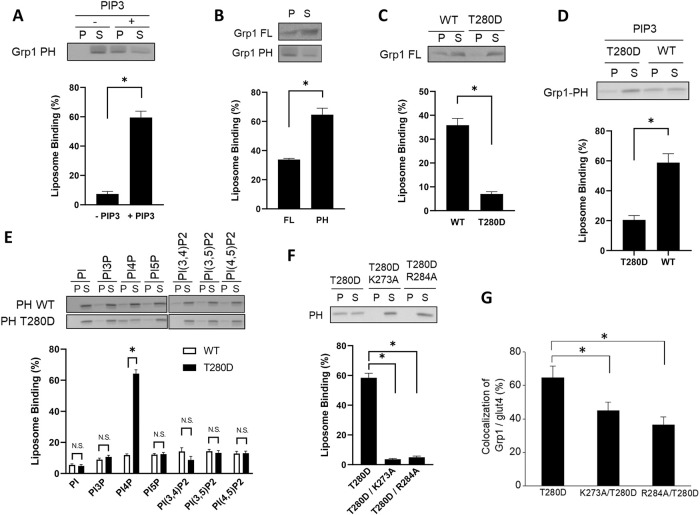
FIGURE 1:
T280 phosphorylation induces Grp1 to recognize a new phosphoinositide. Quantitative results are shown as mean with standard error: *, p < 0.05, NS p > 0.05, Student’s t test. The number of independent experiments performed is specified below. (A) PIP3-dependent recruitment of the Grp1 PH domain to liposomal membrane. The PH domain was incubated with liposomes containing PIP3, or not, followed by centrifugation to detect distribution in the pellet (P) vs. supernatant (S). A representative result along with quantitation from four experiments is shown. (B) Full-length Grp1 shows reduced recruitment to PIP3-containing liposomes as compared with that of the PH domain. Constructs as indicated were incubated with PIP3-containing liposomes, followed by centrifugation to detect distribution in the pellet (P) vs. supernatant (S). A representative result along with quantitation from three experiments is shown. (C) The T280D mutation further reduces the recruitment of full-length Grp1 to PIP3-containing liposomes. Grp1 constructs as indicated were incubated with PIP3-containing liposomes, followed by centrifugation to detect distribution in the pellet (P) vs. supernatant (S). A representative result along with quantitation from four experiments is shown. (D) The T280D mutation also reduces the recruitment of the PH domain of Grp1 to PIP3-containing liposomes. PH domain constructs as indicated were incubated with PIP3-containing liposomes, followed by centrifugation to detect distribution in the pellet (P) vs. supernatant (S). A representative result along with quantitation from four experiments is shown. (E) The T280D mutation induces the Grp1 PH domain to recognize PI4P. Liposomes were generated with major lipids of organellar membrane along with a particular phosphoinositide, PI3P, PI4P, PI5P, PI(3,4)P2, PI(3,5)P2, or PI(4,5)P2. The different liposomes were then incubated with PH domain constructs as indicated, followed by centrifugation to detect distribution in the pellet (P) vs. supernatant (S). A representative result along with quantitation from three experiments is shown. (F) Mutating key residues in the phosphoinositide-binding pocket of the Grp1 PH domain prevents its recruitment to PI4P-containing liposomes. PH domain constructs as indicated were incubated with PI4P-containing liposomes, followed by centrifugation to detect distribution in the pellet (P) vs. supernatant (S). A representative result along with quantitation from three experiments is shown. (G) Mutating key residues in the binding pocket of the PH domain reduces the localization of the Grp1-T280D at the recycling endosome. Adipocytes were stably transfected with constructs as indicated, and then the colocalization of different constructs with internal glut4 (marker for the recycling endosome in adipocytes) was quantified; n = 10 cells per experiment.