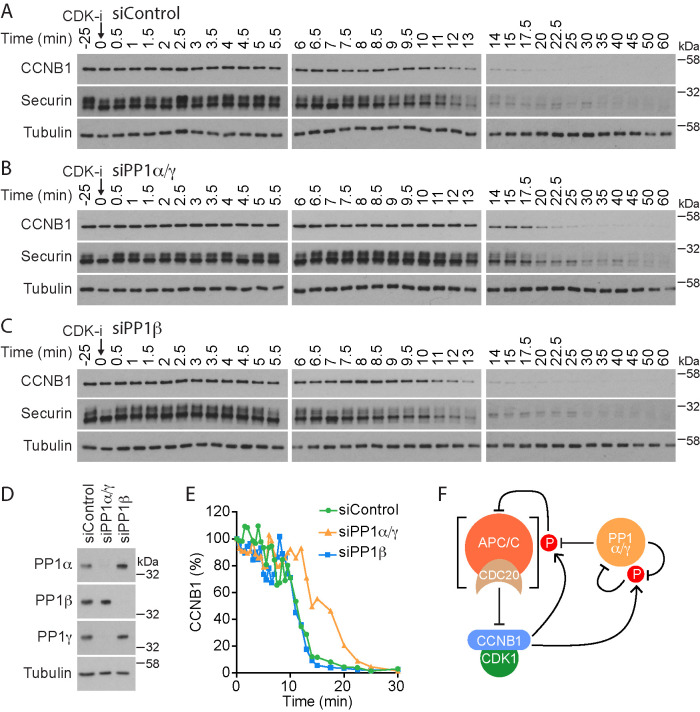
FIGURE 2:
Identification of the major PP1 isoforms counteracting CDK1 regulation of APC/C. (A–C) HeLa cells were either (A) treated with control siRNA (siControl) or depleted for catalytic subunits of (B) PP1α/γ (PP1α/γ) or (C) PP1β (PP1β) and then arrested in mitosis. Mitotic exit was then triggered by CDK1 inhibition (CDK-i), and samples were taken for Western blot at the times indicated. (D) Western blot confirming efficient depletion of PP1 catalytic subunits. (E) CCNB1 levels were measured as a function of time in siControl, siPP1α/γ, and siPP1β for the representative experiments shown in A–C and plotted in the line graph. (F) Schematic depicting the potential role of PP1 in counteracting inhibitory CDK1-cyclin B phosphorylation of APC/CCDC20. CDK1-cyclin B phosphorylation also inhibits PP1 activity, and PP1 reactivates via an autocatalytic process. These are all freely reversible reactions. Activated APC/CCDC20 feeds back to irreversibly inhibit CDK1-cyclin B by promoting cyclin B destruction.