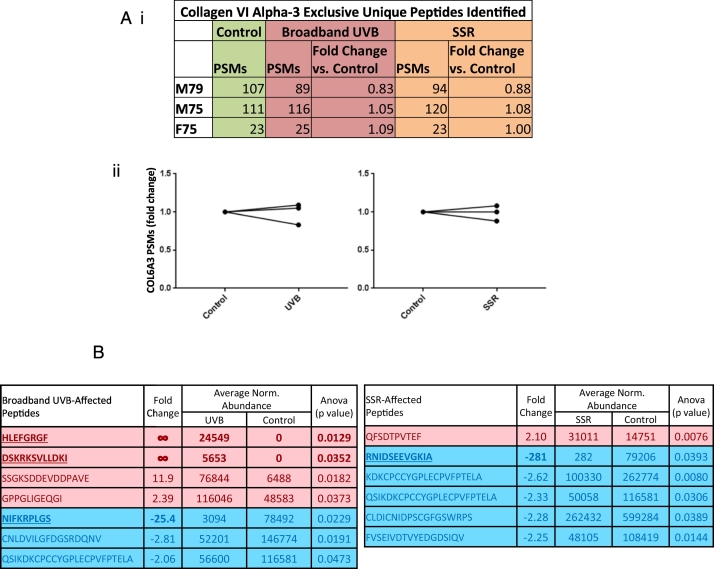
Fig. 4.
UV irradiation of HDF-derived microfibril isolations did not cause changes to the overall proteolytic susceptibility of COL6A3. PSMs for broadband UVB- and SSR -irradiated COL6A3 per individual and their fold changes in comparison to control COL6A3 are shown (Peptide Prophet FDR ≤ 5%) (Ai). In contrast to fibrillin-1, both broadband UVB- (Aii, left panel) and SSR-irradiation (Aii, right panel) failed to cause any consistent change in the number of COL6A3 peptides identified (average change = 0.99 for both UVB and SSR). However, data-dependent peptide quantification did reveal significant changes in the relative abundance of COL6A3 peptide sequences post-UVR exposure. Only peptides with fold changes greater than or equal to two were considered (B; N = 3). Seven COL6A3 peptides in broadband UVB-irradiated microfibril samples and six in SSR-irradiated samples were significantly increased (red) or decreased (blue) in relative abundance compared to control samples. Peptide sequences, fold changes relative to the control group, average normalised abundances and p values are shown (Progenesis multivariate paired ANOVA). Peptide sequences with fold changes greater than twenty are in bold and underlined.