Figure 3. FA and CR reverse correlations:
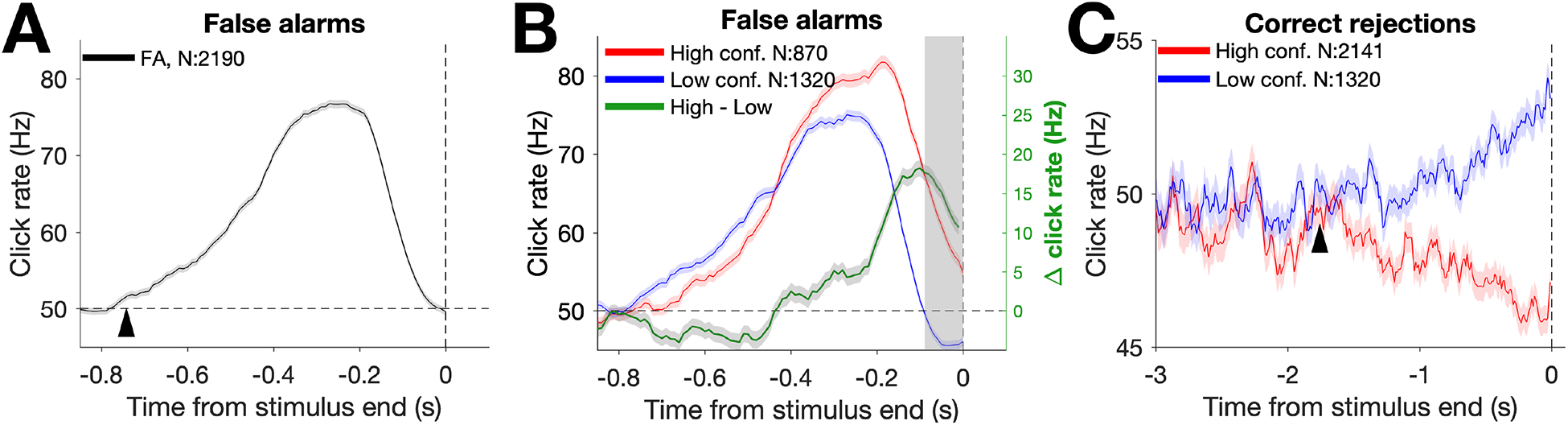
Combined data from 7 subjects was used to calculate average click rate over time for each outcome. RC traces were constructed by convolving click times preceding outcomes with causal half-Gaussian filters (σ = 0.05 s). A, Detection report kernel. RC trace (black line) is comprised of all FA trials, showing the average click rate preceding FAs. The start of the detection report kernel (arrow) was estimated by fitting the ascending phase of the kernel with a 2-piece linear function with 3 free parameters: the baseline click rate (left of arrow), the slope of the kernel’s ascending phase (right of arrow), and the start of the ascending phase (arrow). Horizontal dotted line denotes the 50 Hz baseline generative click rate. B, Detection report confidence kernels. RC traces show the average click rate preceding high (red) and low (blue) confidence FAs, as well as the difference in click rate between the two confidence kernels (high - low; green). Same conventions as in A. The shaded portion of the graph near time 0 shows the temporal interval analyzed in Figure S3A. C, CR confidence kernels. As in B, but showing RC traces preceding CRs. The divergence point between the two confidence kernels (arrow) was estimated by fitting the difference between the two kernels (high - low; CR confidence difference kernel) with a 2-piece linear function with 2 free parameters (see Figure S2, column 4 for fits): the divergence point from a baseline difference of 0 Hz (arrow) and the slope from that point onward. For all kernels, shaded region shows +/− SEM. N = number of trials for each trace. See Figure S2 and S3.
