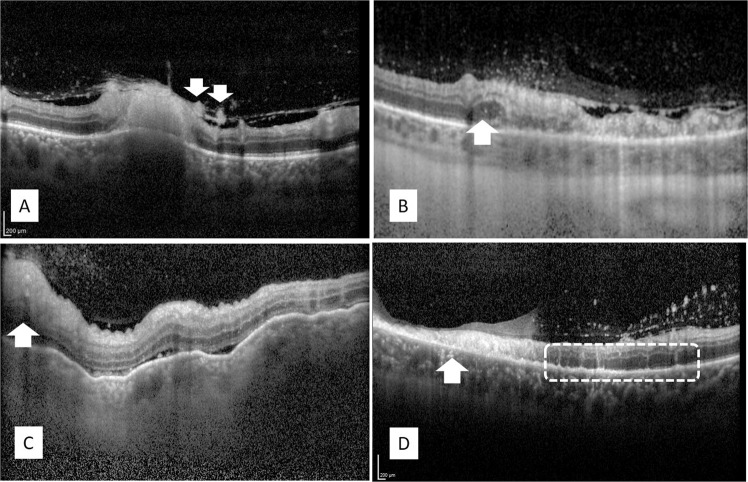
Fig. 6. OCT characteristics of infectious retinitis.
a Toxoplasma retinochoroiditis: full-thickness hyperreflectivity of the retinal lesion with shadowing and thickening of the underlying choroid and hyperreflective round deposits along the posterior hyaloid (arrows); b syphilitic retinitis: full-thickness retinal hyperreflectivity and disruption of retinal layers, posterior hyaloidal deposits, and outer nuclear layer thickening at the advancing edge of the lesion (arrow); c VZV necrotizing retinitis: full-thickness retinal hyperreflectivity with overlying vitreous cells (arrow), advancing with diffuse inner retinal hyperreflectivity, shallow subretinal fluid, and RPE undulations with thickened choroid; d CMV retinitis: Thinned retina with full-thickness retinal hyperreflectivity and disruption of retinal layers (arrow), posterior hyaloidal hyperreflective dots, and hyperreflective vertical strips within the outer nuclear layer between the necrotic and healthy retina (indicated by a rectangle), and hyperreflective dots in the choroid.