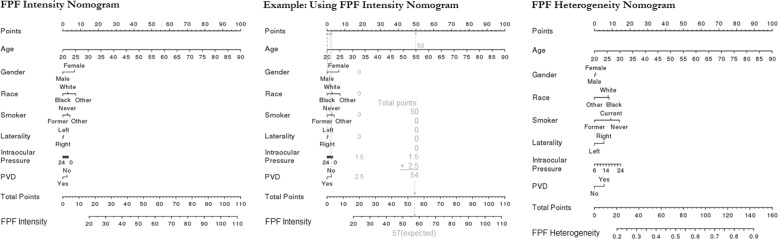
Fig. 6. Nomograms for flavoprotein fluorescence (FPF) intensity and FPF heterogeneity in healthy control patients.
Based on these nomograms, demographic and ocular factors are used to calculate expected FPF intensity and FPF heterogeneity for a given patient. To use the nomogram, the number of points corresponding to each factor are added together, and the total points are mapped to the expected FPF value. For example, the center panel shows how the FPF intensity nomogram (left) would be used for a 55-year-old male, Black, former smoker whose right eye was imaged, and who has intraocular pressure of 12 mmHg and no history of posterior vitreous detachment (PVD).