Fig. 2.
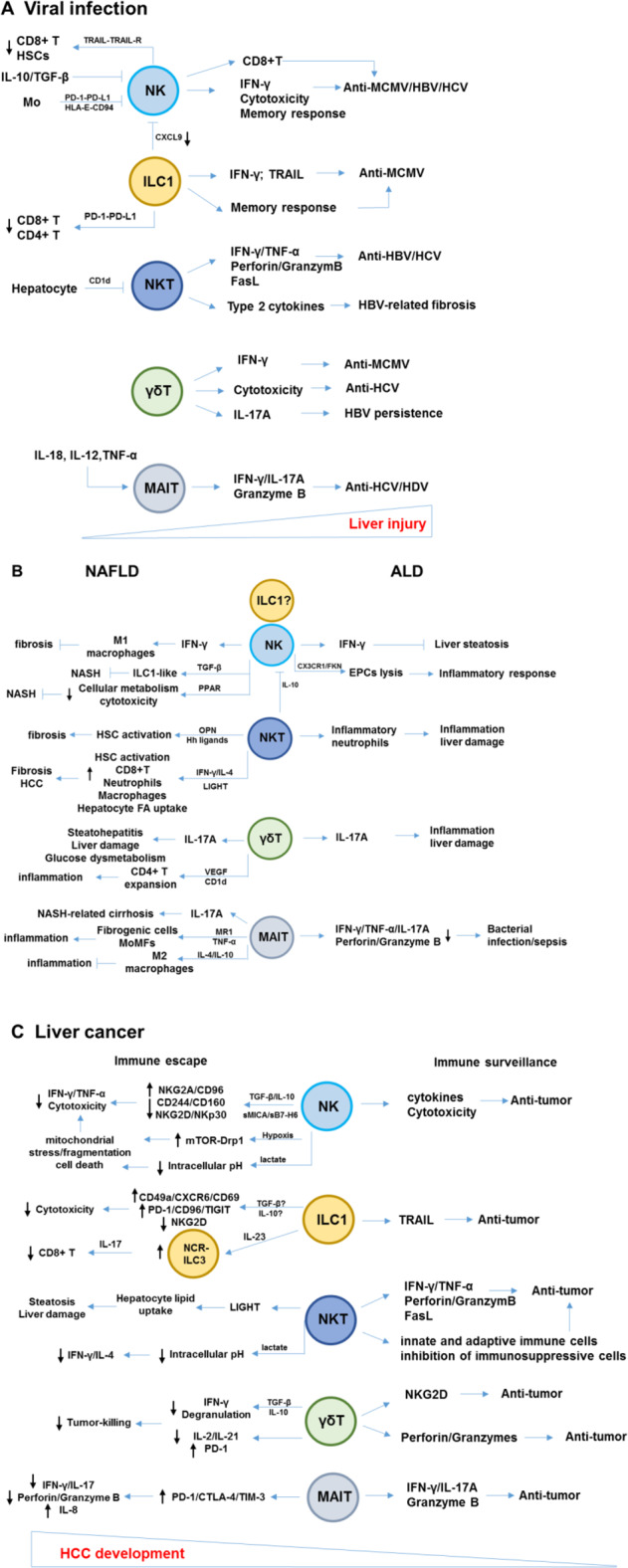
Pathological and protective roles of innate lymphocytes in liver diseases. a During viral infection of the liver, innate lymphocytes play critical antiviral roles via several mechanisms, including cytokine production, cytotoxicity, activation of adaptive immune cells, and memory responses; however, these antiviral functions may be inhibited by suppressive immune cells or cytokines in the virus-infected liver. Furthermore, innate lymphocytes, particularly NK cells and ILC1s, play an important role in the regulation of adaptive immune responses to maintain immune homeostasis. b The pathological responses of innate lymphocytes during the progression of ALD and NAFLD. NK cells exhibit protective roles in preventing liver steatosis and fibrosis. c Immunosurveillance of innate lymphocytes in liver cancer. In tumor microenvironments, a series of factors induce the dysfunction and exhaustion of innate lymphocytes, resulting in immune escape. NK natural killer, ILC innate lymphoid cell, NKT natural killer T, MAIT mucosal-associated invariant T cells. OPN osteopontin, Hh hedgehog, LIGHT LTβR ligand, PPAR peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor, MR1 MHC class-I-related molecule 1, EPCs endothelial progenitor cells, mTOR-Drp1 rapamycin-GTPase dynamin-related protein 1
