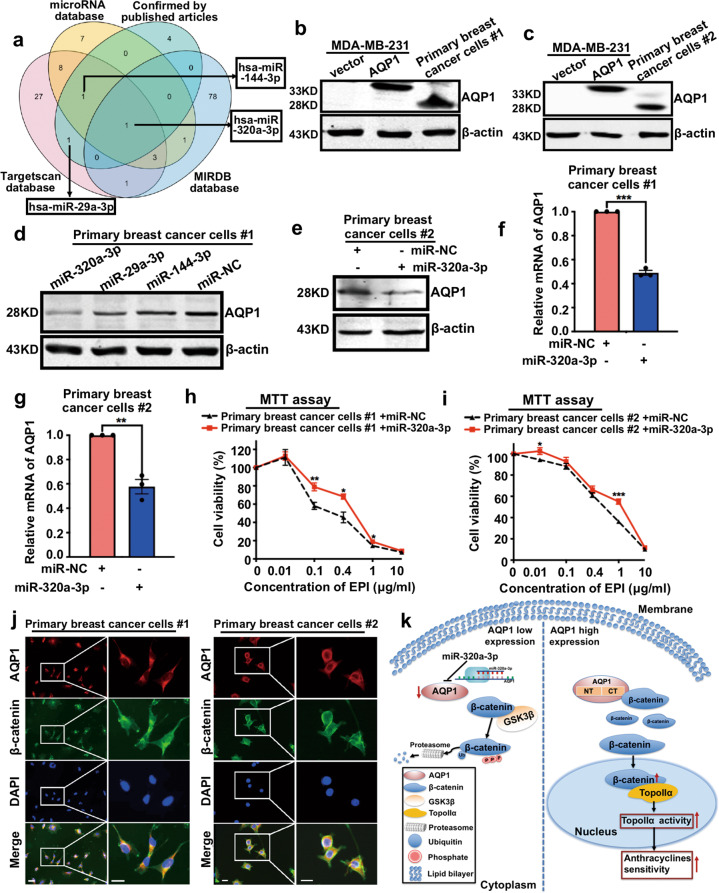
Fig. 7. miR-320a-3p attenuates EPI chemosensitivity by inhibiting AQP1 expression in breast cancer.
a A Venn diagram showed several candidate microRNAs potentially regulating AQP1 based on a combination analysis of three public databases and verified data retrieved from published literature. b, c Western blot of AQP1 expression in primary breast cancer cells #1 (b) and #2 (c), vector/MDA-MB-231 and AQP1/MDA-MB-231 cells. β-actin was the loading control. d, e AQP1 expression was detected in primary breast cancer cells #1 (d) and #2 (e) transfected with microRNAs by western blot analysis. β-actin was the loading control. f, g The mRNA level of AQP1 was detected in miR-NC/primary breast cancer cells and miR-320a-3p/primary breast cancer cells by RT-qPCR. GAPDH was as control. (two-tailed Student’s t test, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). h, i The viability of miR-NC/primary breast cancer cells and miR-320a-3p/primary breast cancer cells with different concentration of EPI treatment for 48 h was detected by MTT assay. Values were expressed as mean ± SEM (two-tailed Student’s t test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). j Co-localization of AQP1 and β-catenin in primary breast cancer cells. Insets showed a high-magnification view of the indicated region. Scale bars: 100 μm. k The signaling pathways of miR-320a-3p/AQP1 axis function in anthracycline chemotherapy. Experiments b–j were independently repeated for three times.