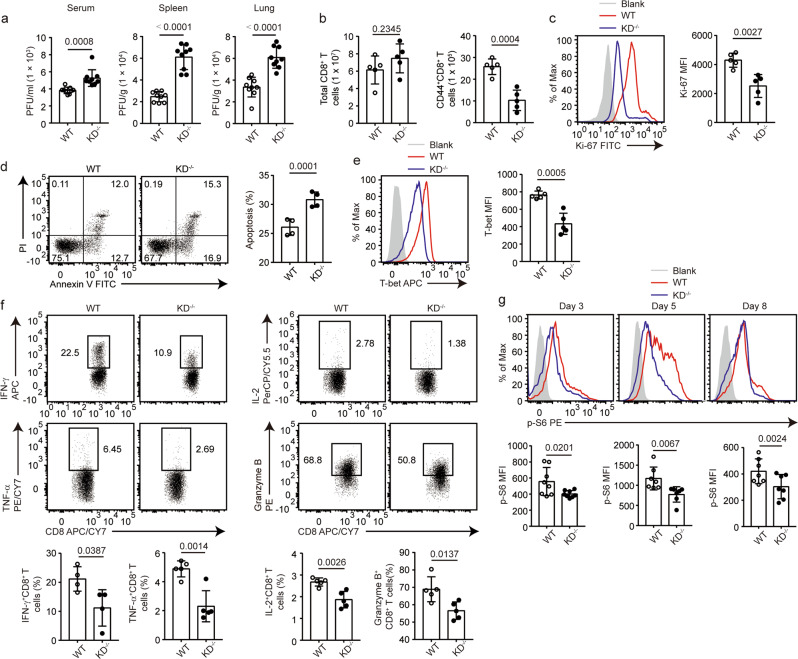
Fig. 5.
DAPK1 regulates proliferation, apoptosis, and cytotoxicity of CTLs during acute viral infection. WT and DAPK1-KD-deficient mice were infected with 2 × 105 PFU LCMV-Armstrong virus i.p. a At 5 dpi, sera, spleens, and lungs were collected from infected WT and KD-deficient mice (n = 9). Viral RNAs were extracted, and tissue viral loads were determined by quantitative RT-PCR. b Numbers of splenic total CD8+ T cells and CD44+CD8+ T cells in WT and KD-deficient mice at 8 dpi with LCMV. The expression of Ki-67 (c), percentage of apoptosis (d), expression of T-bet (e), and the frequencies of IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2, and granzyme B (f)-producing cells in splenic CD44+CD8+ T cells at 8 dpi with LCMV were determined by flow cytometry. Phosphorylation of S6 (g) in splenic CD44+CD8+ T cells was determined by phosflow staining at 3, 5, and 8 dpi with LCMV. The data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments (b–g, n = 5). Statistical significance was measured by the unpaired Student’s t test. Error bars are the mean ± SD