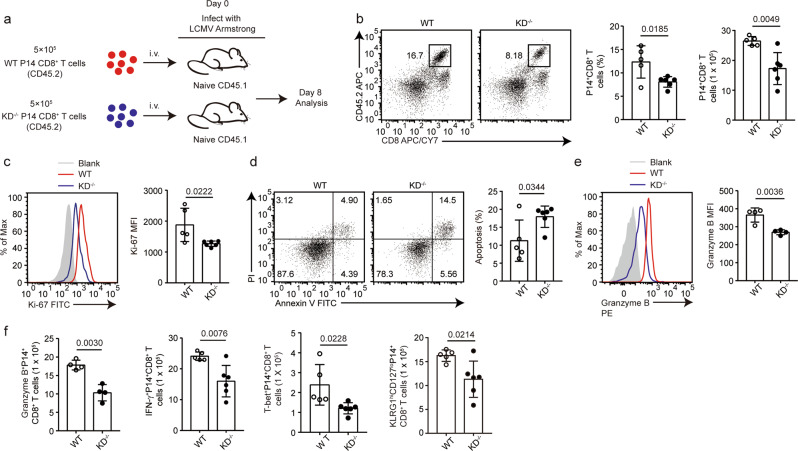
Fig. 6.
DAPK1 promotes antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell responses during acute viral infection. a Antigen-specific P14+CD8+ T cells were purified with magnetic beads from P14; CD45.2 (P14-WT) and P14; CD45.2; CD4-Cre; Dapk1-KDfl/fl mice (P14-KD-deficient) mice. On day 0, 5 × 105 WT P14+CD8+ T cells or KD-deficient P14+CD8+ T cells were injected i.v. into C57/B6J CD45.1 recipient mice. After 12 h, the recipient mice were infected i.p. with LCMV-Armstrong (2 × 105 PFU) virus for 8 days. b Frequency and number of splenic P14+CD8+ T cells in recipient mice. The expression of Ki-67 (c), percentage of apoptosis (d), and expression of granzyme B (e) in WT P14+CD8+ T cells or KD−/− P14+CD8+ T cells recovered from recipient mice were determined by flow cytometry. f The numbers of granzyme B+, IFN-γ+, T-bet+, and terminal effective (KLRG1highCD127low) WT P14+CD8+ T cells or KD−/− P14+CD8+ T cells were quantified. The data shown are representative of at least two independent experiments (n ≧ 5 per group). Statistical significance was measured by the unpaired Student’s t test. Error bars are the mean ± SD