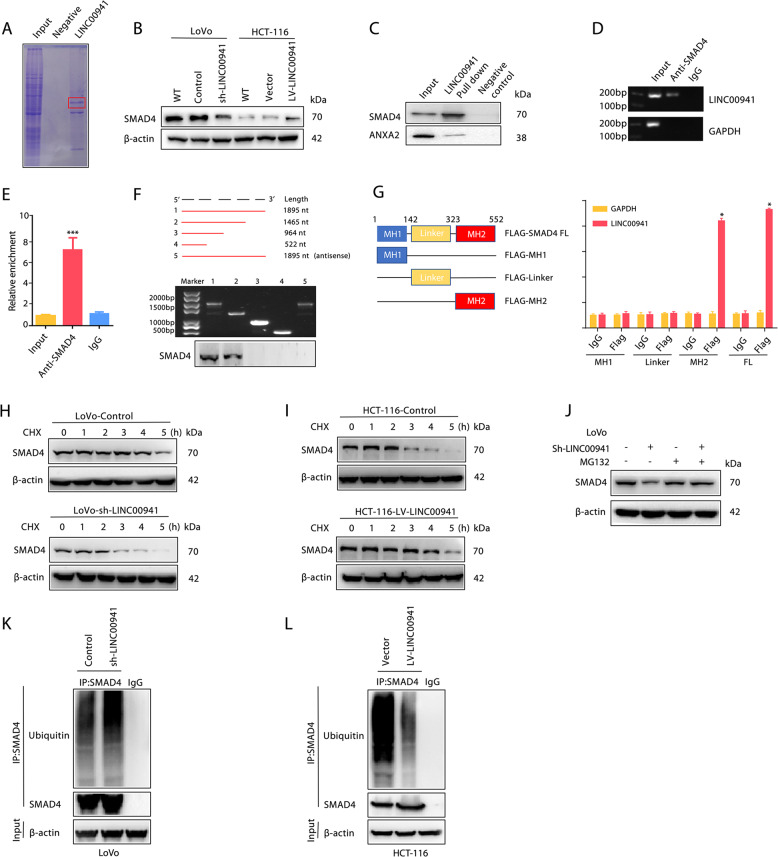
Fig. 3. LINC00941 promotes SMAD4 protein stability.
a Coomassie blue staining showing the results of an RNA pulldown assay with LINC00941. b The expression of SMAD4 in LoVo cells with or without LINC00941 knockdown or in HCT-116 cells with or without LINC00941 overexpression was determined by Western blotting. β-Actin was used as a loading control. c RNA pulldown assay with LINC00941, followed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. ANXA2 was used as a loading control. RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay for SMAD4 followed by agarose gel electrophoresis (d) and qRT-PCR (e) revealed that LINC00941 could bind the SMAD4 protein. f RNA pulldown assay for full-length or truncated LINC00941 and the indicated antisense probe, followed by Western blotting using the SMAD4 antibody. g RIP assay for Flag-tagged full-length or truncated SMAD4 protein, followed by qRT-PCR assay for LINC00941. The half-life of SMAD4 in LoVo cells with or without LINC00941 knockdown (h) or in HCT-116 cells with or without LINC00941 overexpression (i). Cells were treated with cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated times; then, SMAD4 levels were analyzed by Western blotting. β-Actin was used as a loading control. j The expression of SMAD4 in LoVo cells with the indicated treatment was determined by Western blotting. The cells were treated with MG132 to inhibit the proteasome. Western blot analysis of ubiquitinated SMAD4 immunoprecipitated from LoVo cells with or without LINC00941 knockdown (k) or HCT-116 cells with or without LINC00941 overexpression (l). The cells were treated with MG132 to inhibit the proteasome. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.