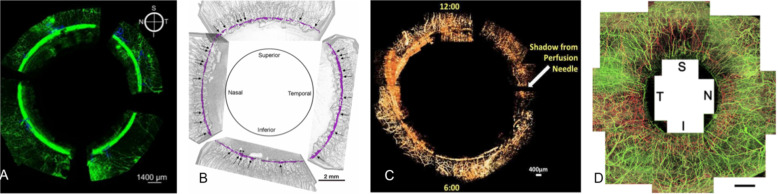
Fig. 3. Three-dimensional reconstructions of the human aqueous outflow system using multiple structural imaging techniques.
a Ribbon-scanning confocal microscopy (collector channels in blue). b 3D micro-CT reconstruction demonstrating Schlemm’s canal (purple ring) with narrowing superiorly in a perfused eye. Black arrows represent sites of collector channels evenly distributed throughout the circumference of the eye. c Virtual casting reconstruction of collector channels from an actively perfused in situ human eye imaged with SD-OCT. d OCT-A reconstructed image of merged superficial (green) and deep (red) vascular networks. Aqueous-carrying vessels are not identifiable. a Adapted image reprinted from Loewen et al. [22]. with permission under the terms of the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). b Adapted image reprinted from [28], with permission from Elsevier. c Adapted image reprinted from [33], with permission from Elsevier. d Adapted image reprinted from [38], with permission from Elsevier.